What is a swivel joint – A Comprehensive Industry Innovations Guide
Introduction
In the modern industrial world, the efficient transfer of fluids, gases, and other media plays a critical role in productivity and safety. One component that makes this possible across countless systems is the swivel joint.
So, what is a swivel joint?
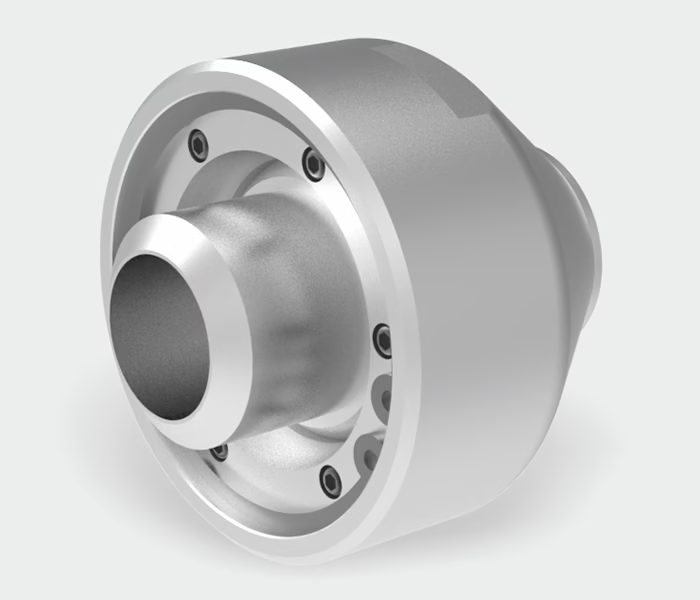
A swivel joint (also known as a rotary joint, rotary coupling, or rotary union) is a mechanical device that allows the rotation of a connection between stationary and moving parts, enabling the smooth and leak-free transmission of fluids or gases.
Swivel joints are essential in industries such as hydraulics, oil and gas, chemical processing, food and beverage, manufacturing, and robotics. They help improve performance, extend equipment life, and reduce maintenance downtime.
In this guide, we will explore the types, functions, materials, applications, and innovations related to swivel joints — offering engineers and buyers a comprehensive resource for understanding their importance in modern industry.

1. Understanding What a Swivel Joint Does
A swivel joint enables two connected parts to rotate relative to one another while maintaining a sealed fluid or gas path.
In simple terms, it allows flexible movement without twisting hoses or damaging pipelines. For example, in hydraulic systems, swivel joints help prevent hose kinking, which can cause leaks or system failures.
Key Functions:
-
Allow rotation or oscillation between components
-
Enable fluid, air, or gas transfer without leakage
-
Reduce hose stress and fatigue
-
Improve system flexibility and lifespan
Common Media Transferred:
-
Hydraulic oil
-
Compressed air
-
Steam or water
-
Coolant
-
Gas and slurry
Typical Working Conditions:
Swivel joints are designed to withstand high pressures, variable speeds, and extreme temperatures, depending on the application. Some advanced designs can handle pressures over 400 bar or temperatures exceeding 250°C.
2. How Does a Swivel Joint Work?
A swivel joint operates using sealing mechanisms and bearings to maintain smooth movement under load.
Inside the housing, O-rings or mechanical seals prevent fluid leakage, while ball bearings or sleeve bearings support the rotational motion. The inner and outer parts rotate independently, ensuring reliable performance even under dynamic pressure.
Basic Components:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Body/Housing | The main structure, typically made from stainless steel, carbon steel, or brass |
| Shaft | Connects to the rotating component and transfers media |
| Seals (O-ring or mechanical seal) | Prevent leakage during operation |
| Bearings | Support rotation and reduce friction |
| End Connections | Threaded, flanged, or custom connections to fit pipelines or hoses |
3. Types of Swivel Joints
There are many types of swivel joints, each suited for different operating conditions and industries.
a. Single Passage Swivel Joint
Used when only one medium (e.g., air or oil) needs to pass through. Common in hydraulic systems or pneumatic tools.
b. Multi-Passage Swivel Joint
Allows multiple channels for transferring different fluids or gases simultaneously. Ideal for robotics, automated machinery, and rotating tables.
c. Hydraulic Swivel Joint
Built for high-pressure hydraulic oil systems, featuring heavy-duty seals and corrosion-resistant materials.
d. Pneumatic Swivel Joint
Designed for compressed air transfer in automation or pneumatic applications. Typically lightweight and made from aluminum or brass.
e. High-Speed Swivel Joint
Engineered for applications with rapid rotation, such as CNC spindles or packaging machinery.
f. High-Temperature Swivel Joint
Made from materials like stainless steel or carbon steel, capable of withstanding steam or hot oil conditions.
4. Design Considerations for Swivel Joints
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
ISO Standards: Compliance with ISO 13709 (petroleum) and ISO 6162 (hydraulics).
Testing: Hydrostatic pressure tests up to 150% of rated capacity.
Leakage Prevention
Seal Life: Calculated using FEA (Finite Element Analysis).
Magnetic Particle Testing: Detecting cracks in welds and seals.
Maintenance and Lubrication
Grease Fittings: Accessible ports for periodic lubrication.
Self-Lubricating Materials: PTFE-coated bearings for low-maintenance systems.
5. Material Selection and Manufacturing
Metals
Stainless Steel 316: Marine/chemical environments (18% Cr, 10% Ni).
Carbon Steel: Cost-effective for hydraulic oil (quenched & tempered to 45 HRC).
Brass: Low-pressure pneumatics (excellent machinability).
Composites & Coatings
PTFE Liners: Reduce the friction coefficient to 0.05–0.10.
Ceramic Coatings: Withstand 1,200°C in kiln applications.
Production Processes
Precision Casting: Investment casting for complex geometries (tolerance ±0.1mm).
CNC Machining: 5-axis milling for sealing surfaces (Ra ≤0.4µm).
Laser Hardening: Increases bearing raceway durability by 300%.
6. Applications of Swivel Joints
Swivel joints are used in a wide range of industrial and commercial systems.
a. Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems
-
Prevent hose twisting and wear
-
Enable flexible connections in moving machinery
b. Oil and Gas Industry
-
Transfer crude oil, drilling mud, and hydraulic fluids in rotating rigs
-
Used in high-pressure swivel stacks
c. Food and Beverage Industry
-
Handle steam, hot water, and cleaning fluids
-
Sanitary-grade stainless steel joints prevent contamination
d. Chemical Processing
-
Transfer aggressive chemicals under controlled conditions
-
Corrosion-resistant designs for long-term reliability
e. Robotics and Automation
-
Enable multiple fluid paths in rotating end effectors
-
Compact designs improve motion freedom and hose routing
f. Marine and Offshore Systems
-
Withstand saltwater corrosion and heavy mechanical loads
-
Used in rotating cranes, loading arms, and underwater systems
7. Key Advantages of Swivel Joints
Swivel joints offer numerous engineering and operational benefits, making them indispensable in industrial applications.
Top Benefits:
-
Leak-Free Operation — High-quality seals maintain integrity under pressure.
-
Extended Hose Life — Reduces bending, twisting, and stress on flexible hoses.
-
Enhanced Flexibility — Enables movement in confined or dynamic setups.
-
Improved Safety — Minimizes risks of hose rupture or fluid leaks.
-
Reduced Downtime — Easy to install, inspect, and replace when necessary.
8. Technological Innovations in Swivel Joint Design
As industries move toward automation and efficiency, swivel joints are evolving with innovative designs and smart materials.
a. Compact and Lightweight Designs
Manufacturers are reducing joint size and weight to suit robotic arms and compact machinery.
b. Multi-Passage Rotary Technology
Allows simultaneous transfer of air, oil, coolant, and data signals, enhancing productivity in automated production lines.
c. Smart Monitoring Integration
Modern designs integrate sensors for pressure, temperature, and leakage detection, improving predictive maintenance.
d. Advanced Sealing Systems
The use of carbon graphite, PTFE, and silicon carbide seals improves performance under extreme conditions.
e. Environmentally Friendly Materials
Eco-friendly lubricants and recyclable materials support sustainable engineering.
9. Future Trends in Swivel Joint Technology
The next generation of swivel joints is driven by automation, Industry 4.0, and sustainability.
Future designs will emphasize:
-
Smart monitoring with IoT connectivity
-
Self-lubricating materials for maintenance-free operation
-
Modular designs for quick customization
-
Higher temperature and pressure ratings
-
Integration with robotic and AI-driven systems
These innovations promise to further enhance efficiency, safety, and operational intelligence across industries.
Conclusion
A swivel joint may seem like a small component, but its impact on system reliability, safety, and efficiency is profound.
From hydraulic systems to automated robotics, these joints ensure seamless rotation and media transfer — making them indispensable in modern engineering.
Understanding what a swivel joint is, how it works, and how to select the right model can help engineers and buyers make informed decisions that optimize system performance and reduce operational costs.
Whether you need a hydraulic swivel joint, multi-passage rotary union, or a custom-designed solution, choosing the right design and material ensures lasting value and precision.