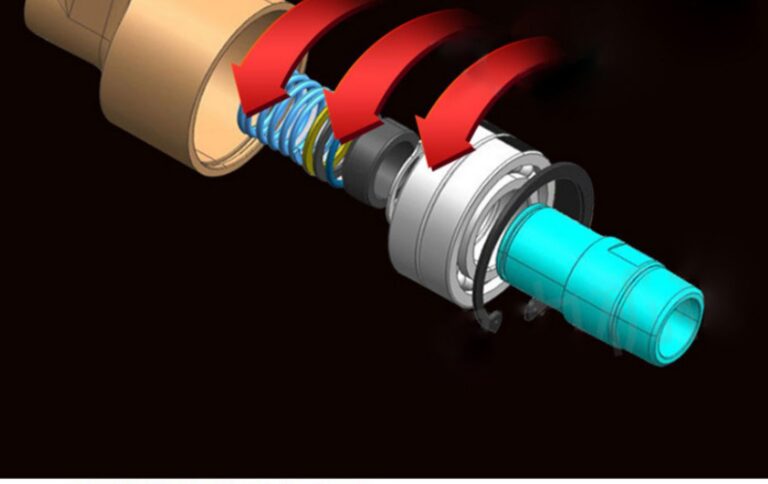
Rotary Union High Pressure Chart
Introduction
In the realm of industrial machinery, rotary unions play a pivotal role in facilitating the transfer of fluids, gases, and power between stationary and rotating components. When dealing with high-pressure applications, understanding the rotary union pressure chart becomes essential. This chart serves as a crucial reference tool that provides valuable insights into the pressure capabilities of different rotary unions, enabling engineers, technicians, and procurement professionals to make informed decisions. In this comprehensive blog post, we’ll delve deep into the world of rotary union high-pressure charts, exploring their significance, how to read them, the factors influencing high-pressure ratings, and much more.
The Significance of Rotary Union High Pressure Charts
A rotary union pressure chart is not just a piece of data; it’s a roadmap for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of industrial equipment. These charts offer a detailed breakdown of the maximum pressure ratings that rotary unions can withstand under various conditions. For industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, and aerospace, where high pressures are the norm, having accurate pressure information is non-negotiable.
Ensuring Equipment Safety
One of the primary functions of a high-pressure chart is to prevent equipment failure due to overpressure. By clearly indicating the maximum pressure a rotary union can handle, it allows operators to set up their systems within safe limits. Overpressurizing a rotary union can lead to catastrophic failures, such as seal ruptures, component fractures, and fluid leaks. These incidents not only cause costly downtime for repairs but also pose significant safety risks to personnel working around the equipment. For example, in the hydraulic system of a large construction excavator, if the pressure exceeds the rating indicated in the rotary union’s high-pressure chart, it could result in a sudden burst of hydraulic fluid, potentially injuring nearby workers.
Optimizing Performance
In addition to safety, high-pressure charts help in optimizing the performance of rotary unions. Operating a rotary union at the right pressure level ensures smooth fluid flow, minimizes friction, and reduces wear and tear on internal components. When you match the pressure requirements of your application with the capabilities of the rotary union, as shown in the chart, you can achieve maximum efficiency. For instance, in a high-pressure waterjet cutting machine, using a rotary union that can handle the exact pressure needed for cutting different materials allows for precise and consistent cuts, enhancing the overall productivity of the machine.
Facilitating Equipment Selection
When procuring rotary unions for new projects or replacing existing ones, the high-pressure chart is an invaluable resource. It enables you to compare the pressure ratings of different models and brands, helping you select the most suitable rotary union for your specific needs. Whether you’re looking for a rotary union for a high-pressure chemical processing plant or a high-speed machining center, the chart provides a quick and easy way to shortlist products that meet your pressure requirements.
How to Read a Rotary Union High Pressure Chart
Reading a rotary union pressure chart may seem intimidating at first, but with a little guidance, it becomes a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the key elements you’ll encounter in most high-pressure charts:
Pressure Rating Column
The most prominent feature of the chart is the pressure rating column. This column lists the maximum pressure values that the rotary union can handle, usually expressed in units such as pounds per square inch (psi), bar, or megapascal (MPa). The pressure ratings are typically categorized based on different operating conditions, such as continuous operation, intermittent operation, or peak pressure. For example, a rotary union might have a continuous operating pressure rating of 3000 psi, an intermittent operating pressure rating of 4000 psi, and a peak pressure rating of 5000 psi. It’s crucial to understand these distinctions as they determine how the rotary union should be used in different applications.
Fluid Type and Compatibility Section
Another important part of the chart is the fluid type and compatibility section. Different fluids have varying chemical properties that can affect the performance and pressure rating of a rotary union. The chart will specify which fluids the rotary union is compatible with and any limitations or precautions associated with each fluid. For instance, a rotary union designed for hydraulic oil may have a different pressure rating when used with a corrosive chemical fluid. Some charts may also include information on the temperature range within which the rotary union remains compatible with specific fluids.
Material and Construction Details
The material and construction of a rotary union significantly impact its pressure-handling capabilities. The high-pressure chart often provides details about the materials used for the body, seals, and other components. For example, a rotary union with a stainless-steel body and fluorocarbon rubber seals will have different pressure and chemical resistance properties compared to one made of brass with nitrile rubber seals. Understanding these material details helps in assessing the durability and suitability of the rotary union for high-pressure applications.
Application Notes and Warnings
To further assist users, many high-pressure charts include application notes and warnings. These notes offer practical advice on how to install, operate, and maintain the rotary union under high-pressure conditions. Warnings highlight potential risks and situations to avoid, such as sudden pressure surges or improper alignment, which could lead to reduced performance or failure of the rotary union.
Factors Influencing Rotary Union High-Pressure Ratings
Several factors come into play when determining the high-pressure ratings of rotary unions. Understanding these factors can help you make more informed decisions when selecting and using rotary unions in high-pressure applications.
Material Quality and Strength
The quality and strength of the materials used in the construction of a rotary union are fundamental to its pressure-handling capabilities. High-grade metals like stainless steel, alloy steel, and titanium are commonly used for the body and internal components of high-pressure rotary unions due to their excellent strength and corrosion resistance. For example, stainless steel is resistant to rust and chemical corrosion, making it suitable for applications involving corrosive fluids. The choice of seal materials also plays a crucial role. High-pressure seals made from materials like polyurethane or PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) can withstand extreme pressures while maintaining a tight seal.
Design and Engineering
The design and engineering of a rotary union are critical in determining its pressure ratings. Advanced design features, such as optimized internal passages, precise machining of components, and proper stress distribution, contribute to the union’s ability to handle high pressures. For instance, a well-designed rotary union will have smooth internal surfaces that reduce fluid turbulence and pressure drop, allowing it to operate efficiently at high pressures. Additionally, the use of advanced engineering techniques, such as finite element analysis (FEA), helps manufacturers simulate and optimize the performance of rotary unions under different pressure conditions during the design phase.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing processes employed also impact the high-pressure ratings of rotary unions. Precise manufacturing techniques, such as CNC machining and heat treatment, ensure that the components are made to exact specifications. CNC machining allows for highly accurate cuts and shapes, resulting in components with tight tolerances. Heat treatment processes can enhance the strength and durability of metals, making them more capable of withstanding high pressures. A rotary union manufactured with subpar processes may have internal defects or dimensional inaccuracies that could compromise its pressure-handling ability.
Assembly and Quality Control
Proper assembly and rigorous quality control are essential for maintaining the high-pressure integrity of rotary unions. During assembly, each component must be installed correctly to ensure a leak-free and stable connection. Quality control measures, such as pressure testing, visual inspections, and material testing, are carried out at various stages of production. For example, a rotary union is typically subjected to a hydrostatic pressure test to verify its pressure-holding capabilities before it leaves the factory. Any flaws detected during quality control are rectified, ensuring that only high-quality, reliable rotary unions reach the market.
Selecting the Right Rotary Union Based on High Pressure Charts
Now that you understand the importance of pressure charts and the factors influencing pressure ratings, let’s explore how to use this knowledge to select the right rotary union for your application.
Identify Your Application Requirements
The first step is to clearly define the requirements of your application. Determine the maximum pressure that the rotary union will encounter during operation. Consider not only the normal operating pressure but also any potential peak pressures or pressure surges. Additionally, identify the type of fluid the rotary union will handle, its temperature range, and the rotational speed of the equipment. For example, if you’re working on a high-pressure oil refining project, you’ll need a rotary union that can handle high temperatures, corrosive oil, and significant pressure fluctuations.
Match Pressure Ratings
Once you have a clear understanding of your application requirements, compare them with the pressure ratings in the high-pressure chart. Look for a rotary union whose maximum pressure ratings exceed your application’s requirements by a safe margin. This buffer ensures that the rotary union can handle unexpected pressure increases without failing. However, avoid choosing a rotary union with a much higher pressure rating than necessary, as it may come with a higher cost and unnecessary complexity.
Consider Other Factors
In addition to pressure ratings, take into account other factors such as fluid compatibility, material construction, connection types, and size. Ensure that the rotary union is compatible with the fluid in your application to prevent chemical reactions or seal degradation. The material construction should be suitable for the operating environment, especially in terms of corrosion resistance and temperature tolerance. Select the right connection type and size to ensure seamless integration with your existing equipment and piping system.
Seek Expert Advice
If you’re unsure about which rotary union to choose, don’t hesitate to seek advice from experts. Manufacturers’ technical support teams, industry consultants, or experienced engineers can provide valuable insights based on their knowledge and experience. They can help you interpret the high-pressure chart, evaluate different options, and make the best decision for your specific application.
Working with Suppliers and Obtaining High-Pressure Charts
When it comes to sourcing rotary unions and obtaining accurate high-pressure charts, establishing a good relationship with reliable suppliers is key.
Research Reputable Suppliers
Start by researching suppliers who have a proven track record in the industry. Look for companies that are known for producing high-quality rotary unions and providing excellent customer service. Online directories, industry forums, and trade shows are great resources for finding potential suppliers. Read customer reviews and testimonials to get an idea of the supplier’s reputation. A supplier with positive feedback is more likely to provide accurate pressure charts and reliable products.
Request Detailed Information
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, reach out to them and request detailed information about their rotary unions, including the high-pressure charts. Ask for clarification on any aspects of the chart that you don’t understand. A good supplier will be willing to answer your questions and provide additional technical data if needed. Some suppliers may also offer customization options, so if your application has specific requirements, discuss them with the supplier to see if they can meet your needs.
Evaluate Supplier Support
In addition to product quality, consider the level of support the supplier offers. A reliable supplier should provide after-sales support, including technical assistance, maintenance advice, and replacement parts. They should also be able to offer guidance on how to use the high-pressure chart effectively and troubleshoot any issues related to the rotary union’s performance under high-pressure conditions.
Maintaining Rotary Unions in High-Pressure Applications
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and continued performance of rotary unions in high-pressure applications.
Regular Inspections
Schedule regular inspections of the rotary union to check for signs of wear, leaks, or damage. Look for any cracks, corrosion, or abnormal vibrations. During inspections, also check the pressure gauges and other monitoring devices to ensure that the rotary union is operating within the specified pressure range as indicated in the high-pressure chart. If any issues are detected, address them promptly to prevent further damage.
Lubrication and Seal Maintenance
Lubricate the moving parts of the rotary union according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear, extending the life of the components. Pay special attention to the seals, as they are crucial for maintaining the pressure integrity of the rotary union. Replace worn-out or damaged seals in a timely manner to prevent leaks. Use seal materials that are compatible with the fluid and operating conditions as specified in the high-pressure chart.
Pressure Monitoring and Control
Implement a system for monitoring and controlling the pressure within the rotary union. Install pressure sensors and regulators to ensure that the pressure remains within the safe and optimal range. Regularly calibrate the pressure monitoring devices to ensure accurate readings. If there are any sudden changes in pressure, investigate the cause immediately and take appropriate corrective actions.
Conclusion
The rotary union high-pressure chart is an indispensable tool for anyone working with high-pressure industrial applications. By understanding its significance, learning how to read it, and considering the various factors that influence pressure ratings, you can make informed decisions when selecting, using, and maintaining rotary unions. Working with reliable suppliers and following proper maintenance practices will further enhance the performance and lifespan of your rotary unions, ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of your industrial equipment. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a procurement professional new to the world of rotary unions, mastering the knowledge related to high-pressure charts is a step towards achieving success in your industrial projects.