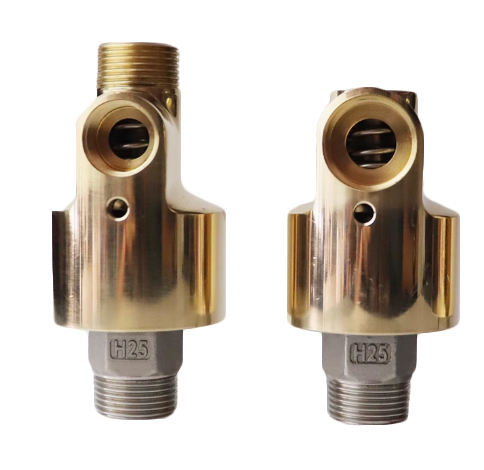
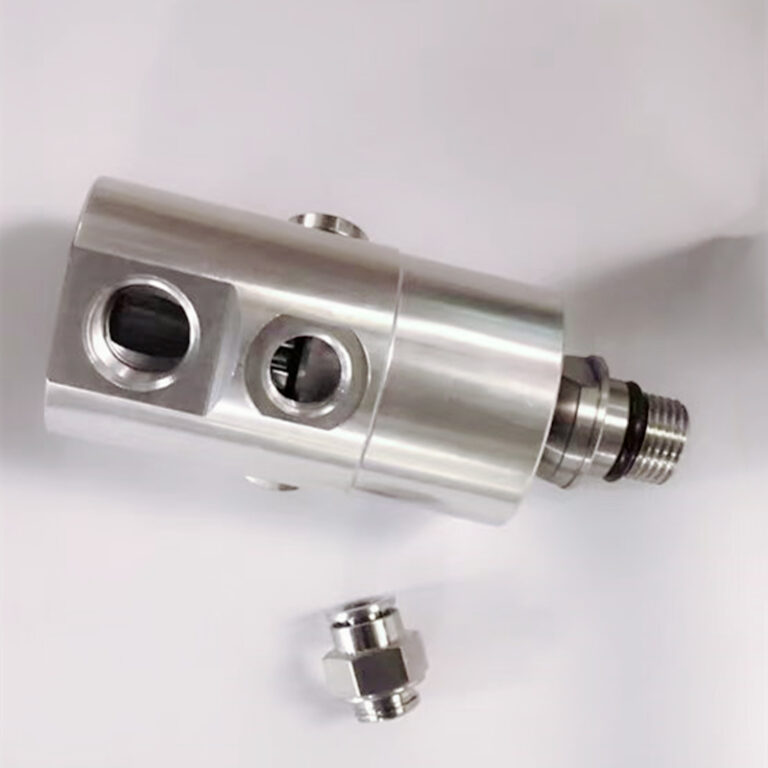
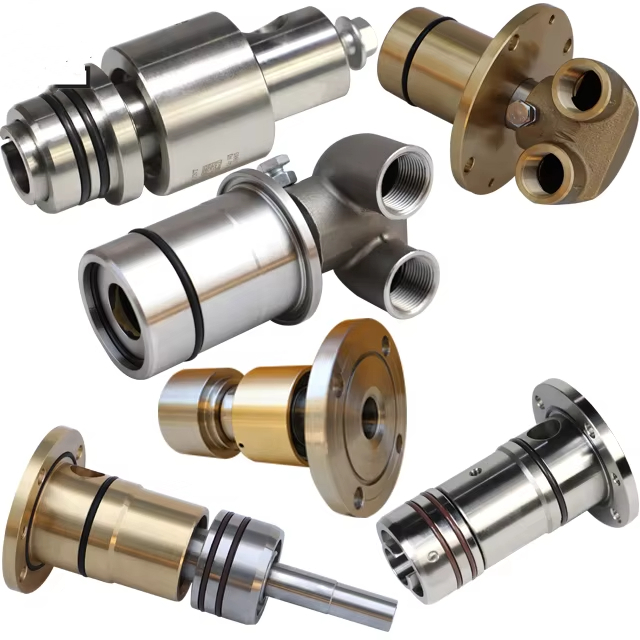
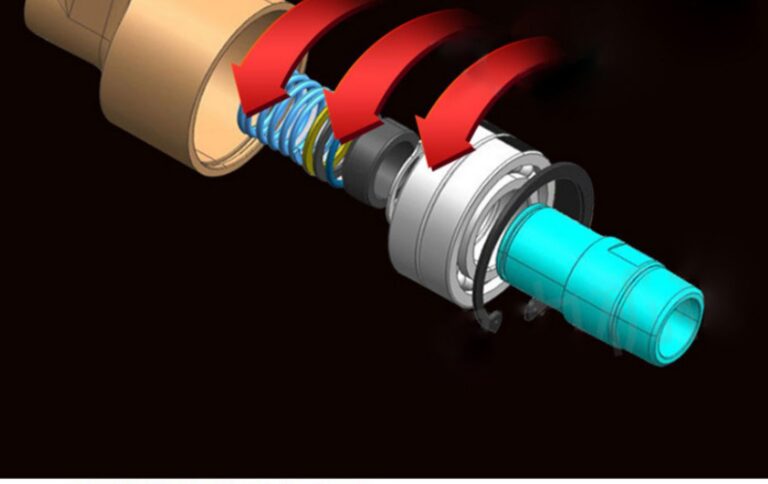
WHAT TYPES OF ROTARY JOINTS ARE AVAILABLE?
Understanding the different types of rotary joints and their specific applications is crucial for selecting the right component for your system. Here’s a detailed overview of each type:
1. Single-way Rotary Joints
– Function: These joints allow fluid transfer in one direction only.
– Applications: Commonly used in simpler systems where only one type of fluid needs to be transferred, such as in single-fluid cooling or lubrication systems.
– Design: Typically consists of a single channel within the housing and shaft, with seals to prevent leakage.
– Advantages: Simple design, easy to install and maintain, cost-effective for basic applications.
2. Double-way Rotary Joints (dual channel rotary joint)
– Function: These dual channel rotary joints enable fluid transfer in both directions without mixing the fluids.
– Applications: Useful in systems where two different fluids need to be transferred independently, such as in dual-circuit hydraulic systems or in processes requiring both supply and return lines.
– Design: Features two separate channels within the housing and shaft, each with its own set of seals to prevent cross-contamination.
– Advantages: Allows for bidirectional fluid transfer, ensuring that fluids remain separate and do not mix.
3. Multi-way Rotary Joints
– Function: These joints can handle multiple fluids simultaneously, directing them into different systems without cross-contamination.
– Applications: Ideal for complex systems where multiple fluids or media need to be managed, such as in multi-channel hydraulic systems, chemical processing, and advanced manufacturing equipment.
– Design: Incorporates multiple channels within the housing and shaft, each with its own set of seals and bearings to ensure that fluids do not mix.
– Advantages: Highly versatile, reduces the number of individual joints required, and simplifies system design.
4. Hydraulic Rotary Unions(hydraulic rotary joint/hydraulic rotary swivel joint)
– Function: hydraulic rotary swivel joint Designed specifically for hydraulic applications, these unions handle high pressures and ensure reliable fluid transfer.
– Applications: Commonly used in heavy-duty hydraulic systems, such as those found in construction equipment, industrial machinery, and automotive applications.
– Design: Built to withstand high pressures and temperatures, often featuring robust seals and bearings to ensure long-term performance.
– Advantages: High pressure capability, durable construction, and reliable performance in demanding environments.
5. Pneumatic Rotary Unions(pneumatic rotary joint/rotary joint for air)
– Function: pneumatic rotary joint is Used for air or vacuum applications, these unions are designed to handle gaseous media.
– Applications: pneumatic rotary joint is Often found in automated machinery, robotics, and pneumatic control systems.
– Design: Typically lighter and smaller than hydraulic rotary unions, with seals and bearings optimized for low-pressure gas applications.
– Advantages: Lightweight, compact, and suitable for high-speed operations, making them ideal for precision control and automation.
Key Considerations for Selection
– Application Requirements: Determine the specific needs of your system, such as the type of fluid, pressure, temperature, and flow rate.
– Material Compatibility: Ensure that the materials used in the rotary joint are compatible with the fluid being transferred to prevent degradation or failure.
– Environmental Conditions: Consider the operating environment, including exposure to contaminants, temperature extremes, and vibration.
– Maintenance and Service Life: Choose a rotary joint that is easy to inspect and maintain, with a long service life to minimize downtime and replacement costs.
– Cost: Balance the initial cost with the long-term benefits, such as reduced maintenance and improved system performance.
Maintenance and Inspection
– Regular Inspections: Check for signs of wear, leaks, or misalignment. Inspect seals, bearings, and the housing for any damage.
– Lubrication: Ensure that bearings and seals are properly lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
– Replacement: Replace worn or damaged components promptly to prevent further issues and ensure the continued performance of the rotary joint.
By carefully considering these factors and selecting the appropriate type of rotary joint, you can ensure that your system operates efficiently, safely, and reliably.