What is a water rotary union?
What is a Water Rotary Union? A Comprehensive Guide
Water rotary unions, also known as rotary joints or rotating unions, are critical components in industrial machinery where fluids like water, steam, or thermal oils must be transferred between stationary and rotating parts. These devices ensure leak-free operation while maintaining pressure and temperature stability, making them indispensable in sectors such as manufacturing, agriculture, and energy.
The working principle of a water rotary union is relatively straightforward yet highly effective. At its core, it consists of two main parts: a stationary housing and a rotating shaft. The stationary housing is connected to the water supply source, while the rotating shaft is attached to the rotating part of the machine. Inside the union, there are seals and bearings. The seals are designed to prevent leakage of water between the stationary and rotating parts, ensuring a tight and efficient connection. The bearings, on the other hand, support the rotation of the shaft, allowing it to turn smoothly with minimal friction.
When water enters the union through the stationary housing, it is directed toward the rotating shaft. The design of the internal channels within the union ensures that the water can flow freely from the stationary part to the rotating part without any disruption, even as the shaft rotates at high speeds. The seals maintain the integrity of the connection, preventing water from escaping and contaminants from entering the system. This continuous and reliable transfer of water is what makes water rotary unions so indispensable in various industrial applications.
In this blog, we’ll explore their functionality, types, and applications, like fluid transfer systems, rotary sealing technology, and high-temperature industrial applications.
1. Understanding Water Rotary Unions: Definition and Functionality
A water rotary union is a mechanical sealing device that connects stationary pipelines to rotating equipment, enabling the transfer of fluids (e.g., water, steam, or hot oil) without leakage. It acts as an interface that accommodates rotational motion while maintaining pressure and temperature integrity.
1.1 Key Components
Stationary Housing: Fixed to the supply line.
Rotating Shaft: Attached to the moving machinery part.
Sealing Mechanism: Prevents fluid leakage and withstands operational stresses. Common materials include carbon graphite, stainless steel, or composite seals.
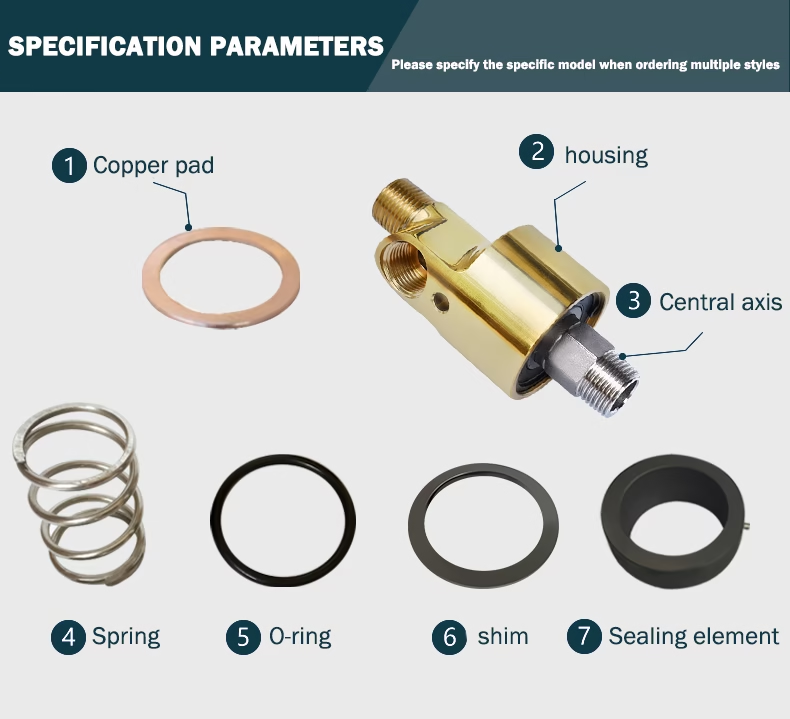 How It Works
How It Works
The union uses precision-engineered seals to create a barrier between static and dynamic parts. For example, the HS-XF080 model employs a steel composite floating seal to enhance corrosion resistance and lifespan, even under high temperatures up to 316°C.
2. Types of Water Rotary Unions
Different designs cater to specific industrial needs. Here are the primary categories:
2.1 By Passage Configuration
Single/Dual-Passage water rotary union: Designed for one or two fluid lines. Deublin’s UNION DUO series supports dual-flow designs for steam and hot oil, with rotational speeds up to 1,500 rpm.
Multi-Passage water rotary union: Transfers multiple fluids simultaneously. The MCPI SAS JR 4/4 model, for instance, offers 4 passages with diameters ranging from 4–18 mm, ideal for complex cooling or hydraulic systems.
2.2 By Application
High-Temperature water rotary Unions: Engineered for steam or diathermic oils. The Re S.p.A. N series uses carbon-graphite bearings to withstand temperatures up to 316°C.
High-Pressure/Vacuum water rotary Unions: The NHP model operates under 400 bar pressure and vacuum conditions, suitable for heavy-duty mining or oil & gas equipment.
2.3 By Material
Stainless Steel rotary union/Brass rotary union: For corrosion resistance.
Cast Iron: Balances durability and cost-effectiveness.
3. Industrial Applications of Water Rotary Unions
3.1 Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing industry, water rotary unions are widely used in processes such as metalworking. For example, in lathes and milling machines, water is often used for cooling and lubricating the cutting tools. A water rotary union enables the supply of water to the rotating cutting tools, ensuring their efficient operation and longevity. It also helps in removing heat generated during the cutting process, which is crucial for maintaining the quality of the machined parts.
In injection molding machines, water rotary unions are used to control the temperature of the molds. By circulating water through the molds, the temperature can be regulated precisely, ensuring consistent and high-quality plastic products. This application also requires a reliable water rotary union to handle the high-pressure water flow and the continuous rotation of the mold components.
3.2 Printing Industry
In the printing industry, water rotary unions play a vital role in offset printing presses. These presses use water-based inks, and a water rotary union is used to supply water to the dampening units. The dampening units moisten the printing plates, which helps in the transfer of ink to the paper. The accurate and continuous supply of water is essential for achieving high-quality prints with sharp images and colors. The water rotary union in this case needs to be able to handle the high-speed rotation of the printing cylinders while maintaining a stable water flow.
3.3 Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, water rotary unions are used in equipment such as bottling machines and food processing machinery. In bottling machines, water is used for cleaning and rinsing the bottles before filling them. A water rotary union allows for the efficient transfer of water to the rotating parts of the machine that handle the bottles. This ensures that each bottle is thoroughly cleaned and ready for filling.
In food processing, water is often used for washing, blanching, and cooling food products. Water rotary unions are used in equipment like conveyors and rotating drums to supply water for these processes. The use of a water rotary union in such applications helps in maintaining the hygiene and quality of the food products, as well as ensuring the smooth operation of the machinery.
3.4 Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, water rotary unions are used in various manufacturing processes. For example, in the production of automotive parts through forging and casting, water is used for cooling the molds and dies. A water rotary union enables the transfer of water to the rotating molds, ensuring that they are cooled evenly and efficiently. This helps in producing high – quality automotive parts with the desired mechanical properties.
Water rotary unions are also used in some automotive testing equipment. For instance, in dynamometers, which are used to test the performance of engines and vehicles, water is used for cooling the braking systems. A water rotary union allows for the continuous supply of water to the rotating components of the dynamometer, ensuring its proper functioning during long-term testing.
4. Advantages of Modern Rotary Unions
4.1 Extended Service Life
Advanced sealing technologies, like steel composite seals, reduce wear and maintenance frequency.
4.2 High-Speed Compatibility
Models like the N series achieve 2,500 rpm, critical for high-speed packaging or textile machinery.
4.3 Easy Maintenance
Modular designs (e.g., Deublin’s replaceable seals) minimize downtime.
4.4 Thermal Stability
Heat dissipation features, such as large discharge ports in the HS-XF080, prevent overheating.
5. Key Selection Criteria
5.1 Selection and Installation
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Water Rotary Union
When choosing a water rotary union for a specific application, several factors need to be considered. First and foremost are the flow rate and pressure requirements. The union should be able to handle the maximum flow rate and pressure of the water in the system. If the flow rate is too high for the selected union, it may cause leakage or inefficient operation.
The rotational speed of the connected parts is also an important factor. Different water rotary unions are designed to operate at different rotational speeds. Selecting a union that can handle the expected rotational speed is crucial for its long-term performance and reliability.
The type of fluid being transferred (in this case, water, but in some cases, water with additives or contaminants) should also be considered. If the water contains particles or chemicals that could be abrasive or corrosive, a union with appropriate materials and sealing mechanisms should be chosen.
The operating temperature of the system is another key factor. As mentioned earlier, if the water is at a high temperature, a high-temperature-rated water rotary union is required.
5.2 Installation Process
The installation of a water rotary union should be carried out carefully to ensure proper functioning. First, the union should be properly aligned with the stationary and rotating parts of the machine. Any misalignment can cause excessive wear on the seals and bearings, leading to premature failure.
The connection to the water supply and the machine should be made securely. This may involve using appropriate fittings and clamps to prevent leakage. During the installation, it is also important to check the integrity of the seals and bearings. If any damage is detected, the union should be repaired or replaced before installation.
After installation, a thorough testing of the water rotary union should be carried out. This includes running the machine at normal operating conditions and checking for any signs of leakage or abnormal operation. Any issues should be addressed immediately to avoid potential problems in the future.
6. Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips
6.1 Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance of water rotary unions is essential for their long-term performance and reliability. This includes periodic inspection of the seals and bearings. The seals should be checked for signs of wear, such as leakage or deformation. If the seals are worn, they should be replaced promptly to prevent water leakage.
The bearings should be lubricated regularly to ensure smooth rotation. The type of lubricant used should be suitable for the operating conditions of the union, taking into account factors such as temperature and rotational speed.
The water supply system connected to the union should also be maintained. This includes checking for any blockages in the pipes or filters that could affect the water flow. Regular cleaning of the water lines can help prevent the build-up of sediment or contaminants that could damage the union.
6.2 Troubleshooting Common Issues
One of the most common issues with water rotary unions is leakage. Leakage can occur due to worn seals, misalignment, or high-pressure fluctuations. If leakage detected, the first step is to check the seals. The leakage persists, the alignment of the union should checked and adjusted if necessary. High-pressure fluctuations can addressed by installing a pressure regulator in the water supply system.
Another common problem is excessive noise or vibration during operation. This can caused by worn bearings, misalignment, or an imbalance in the rotating parts. Worn bearings should replace, and the alignment of the union and the rotating parts should be checke and correct. If an imbalance suspected, the rotating parts should balance.
In some cases, the water flow through the union may be restricted. This can be due to blockages in the internal channels of the union or the water supply lines. Cleaning the union and the water lines can often resolve this issue.
7. Future Trends in Rotary Union Technology
Smart Sensors: Integration with IoT for real-time pressure and temperature monitoring.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Biodegradable seals to reduce environmental impact.
Compact Designs: Miniaturized unions for robotics and aerospace applications.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What industries use water rotary unions most?
A: Industries like paper, chemical, and automotive rely heavily on them for fluid transfer to rotating machinery.
Q: How do I know if a water rotary union is failing?
A: Signs include leaks, increased noise, or reduced fluid flow.
Q: Can water rotary unions handle high-pressure applications?
A: Yes, specialized models are design for pressures exceeding 5,000 PSI.
Conclusion
Water rotary unions are an essential component in many industrial applications. They enable the reliable transfer of water between stationary and rotating parts of machinery, ensuring the smooth operation of various processes. Understanding the definition, working principle, applications, types, selection, installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of water rotary unions is crucial for anyone involved in industries that rely on such equipment. By choosing the right water rotary union, installing it correctly, and maintaining it regularly, industries can enhance the efficiency and productivity of their operations while minimizing downtime and costs associated with equipment failure.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see further improvements in water rotary union design and performance. These advancements will likely lead to more efficient and reliable fluid transfer solutions, opening up new possibilities for industrial applications.







