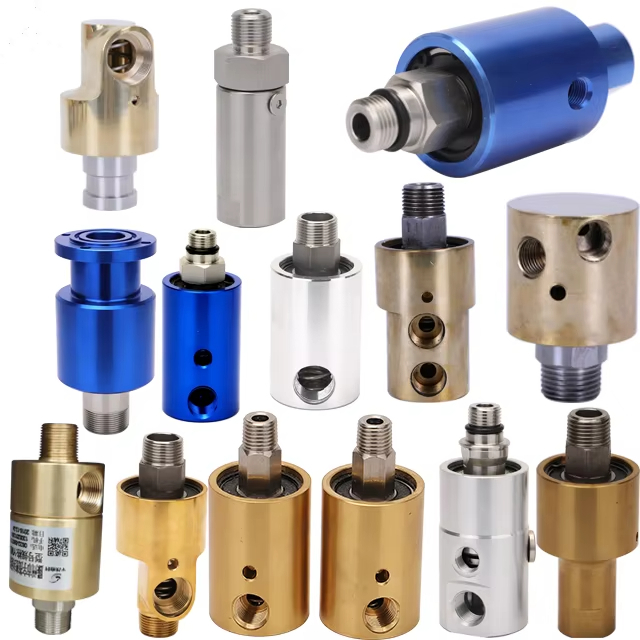
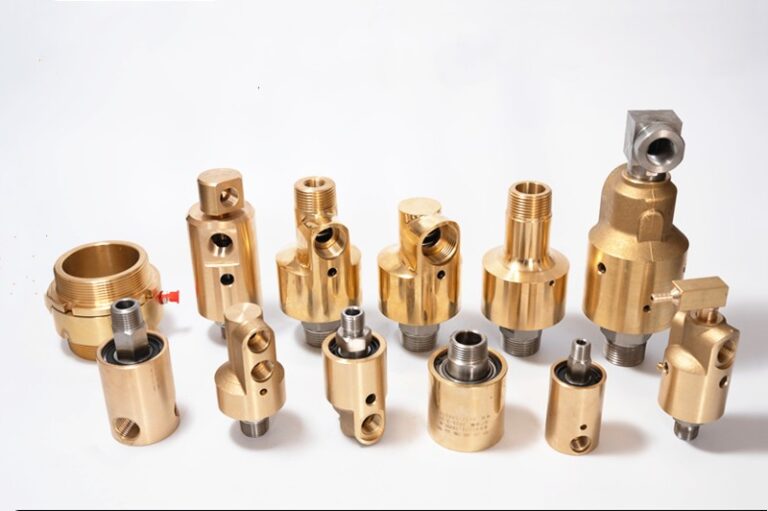
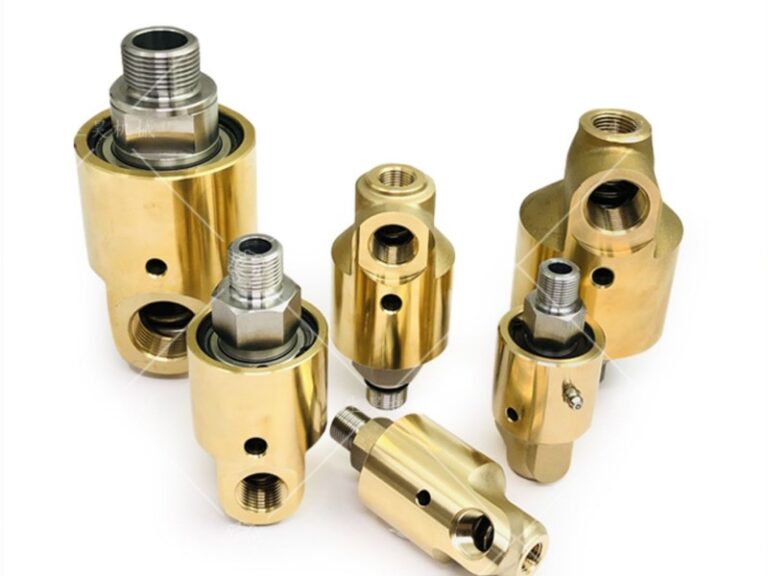
DOES ROTARY UNION BEARING?
A rotary union, also known as a rotating joint or swivel joint, typically includes bearings to allow for smooth and continuous rotation while maintaining a leak-free connection. The bearings in a rotary union play a crucial role in supporting the rotating part and ensuring that the fluid transfer is efficient and reliable. Here’s a more detailed look at the bearings in a rotary union:
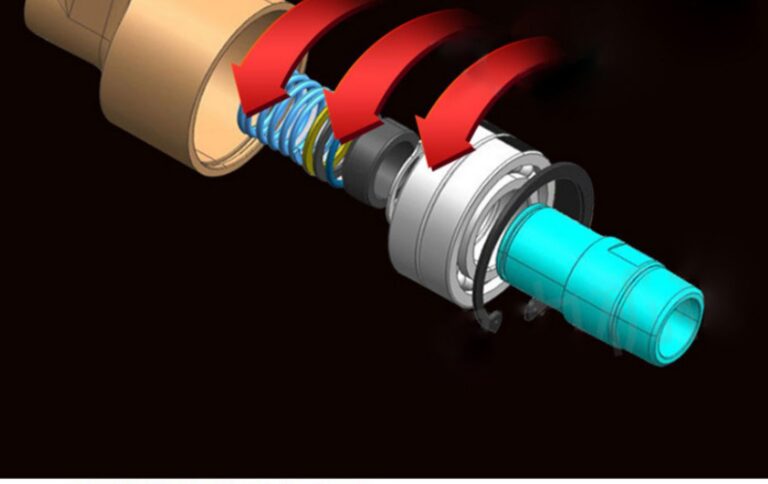
First, what is the “bearing” in the rotary union
“Bearing” in the rotary union means the bearing part used inside the joint. Generally, ball bearings, plain bearings or two-way bearings are used, which have similar designs and materials to bearings, and can improve the axial bearing capacity and mechanical properties of the joint. The main purpose of this “bearing” design is to withstand the axial load of the rotary union during use, thereby reducing the relative displacement and wear between the rotary unions and improving the service life of the joint. In addition, the “bearing” can also improve the seismic performance, safety performance and reliability of the rotary union.
Second, the “bearing” material in the rotary union
The “bearing” in the rotary union, like the bearing, also requires the material to have high strength, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance and other characteristics. Commonly used materials are high-strength steel, heat-treated steel, stainless steel, ceramics and so on. These materials also need to go through high-precision CNC machining, heat treatment, polishing and other processes to achieve satisfactory performance and accuracy requirements.
Third, Types of Bearings in rotary union
1. Ball Bearings:
– Description: Ball bearings are commonly used in rotary union due to their low friction and high efficiency.
– Function: They support radial and axial loads and allow for smooth rotation.
– Materials: Typically made from stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials to withstand harsh environments.
2. Roller Bearings:
– Description: Roller bearings, such as cylindrical or tapered roller bearings, can handle higher loads compared to ball bearings.
– Function: They are suitable for applications with heavy loads and high speeds.
– Materials: Often made from hardened steel or other durable materials.
3. Thrust Bearings:
– Description: Thrust bearings are designed to handle axial loads, which are forces applied parallel to the axis of rotation.
– Function: They are used in applications where there is significant axial load, such as in some types of pumps and compressors.
– Materials: Commonly made from steel or other high-strength materials.
4. Sleeve Bearings (Journal Bearings)
– Description: Sleeve bearings, also known as journal bearings, are simpler in design and consist of a shaft rotating within a sleeve.
– Function: They are often used in applications with lower rotational speeds and lighter loads.
– Materials: Can be made from bronze, brass, or other self-lubricating materials.
Fourth, Functions of Bearings in Rotary Unions
1. Supporting the Rotating Part:
– Role: Bearings support the rotating part of the rotary union, allowing it to rotate smoothly and without excessive wear.
– Benefit: Ensures long service life and reliable operation.
2. Reducing Friction:
– Role: Bearings reduce friction between the rotating and stationary parts, minimizing energy loss and heat generation.
– Benefit: Improves efficiency and reduces wear on the components.
3. Handling Loads:
– Role: Bearings are designed to handle both radial and axial loads, depending on the application.
– Benefit: Ensures that the rotary union can operate under various load conditions without failure.
4. Maintaining Alignment:
– Role: Bearings help maintain the alignment of the rotating and stationary parts, ensuring that the seals remain in proper contact.
– Benefit: Prevents leaks and ensures consistent fluid transfer.
Fifth, how to choose the right “bearing”
When selecting the “bearing” in the joint, it is necessary to determine the specific bearing type, material and size according to the application scenario and requirements of the joint. In general, high-speed rotating joints need to use ball bearings, large load applications need to use two-way bearings, and the joint in a closed environment can use plain bearings.
Maintenance and Considerations
– Lubrication: Proper lubrication is essential to ensure the longevity and performance of the bearings. Many rotary union come with built-in lubrication systems, but regular maintenance and inspection are still necessary.
– Sealing: The seals around the bearings must be maintained to prevent fluid leakage and contamination.
– Temperature and Pressure: Ensure that the bearings are rated for the operating temperature and pressure of the application.
– Material Compatibility: Choose bearings made from materials that are compatible with the fluids being transferred and the environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Bearings are a critical component of rotary union, enabling them to function efficiently and reliably. The type of bearing used depends on the specific application requirements, including the load, speed, and environmental conditions. Regular maintenance and proper selection of bearings are key to ensuring the long-term performance and reliability of the rotary union.