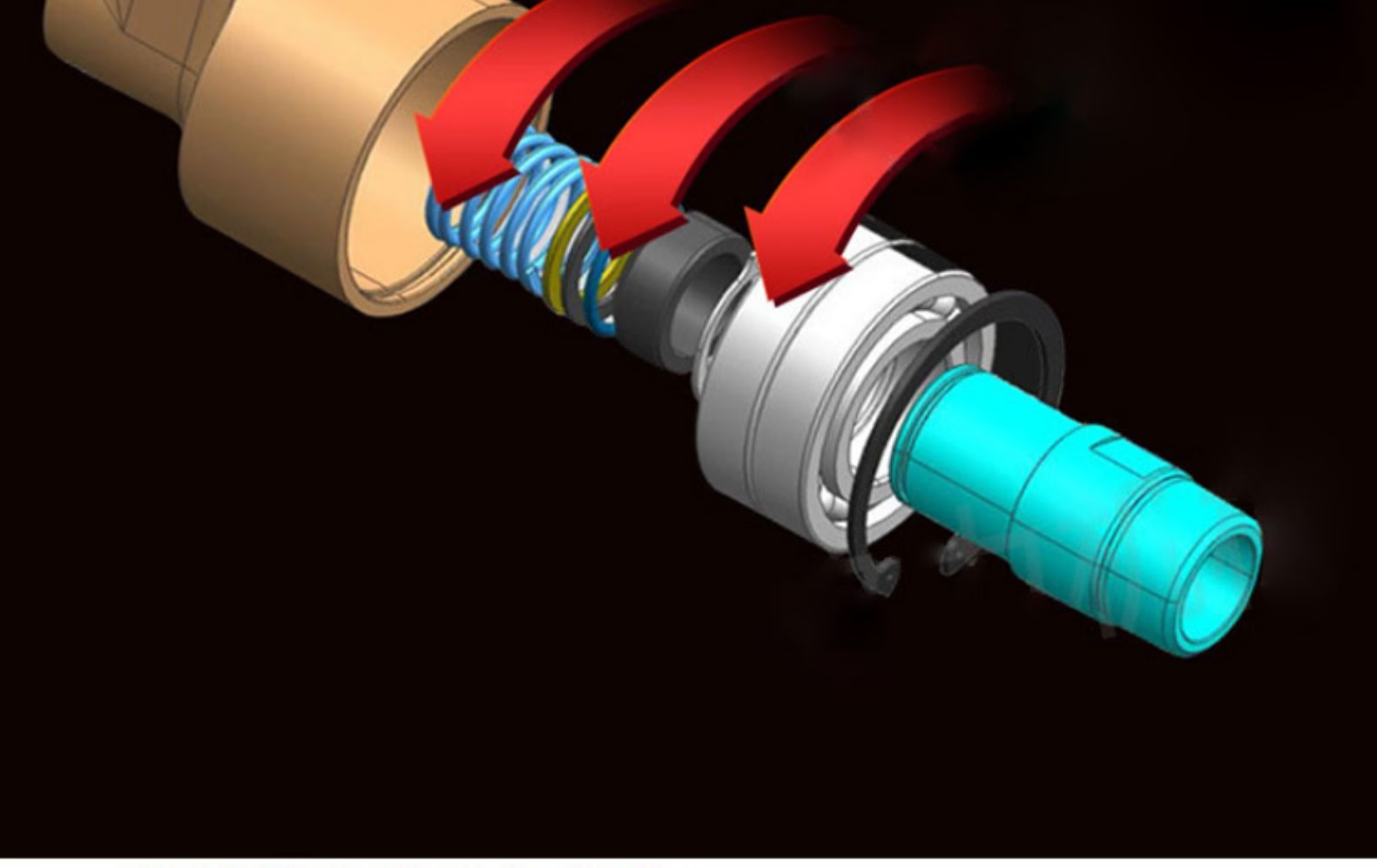
How a rotary union works?
What is a rotary union?
The rotary union is a sealing device that connects rotating parts with fixed pipelines. It is essentially a seal that connects a stationary supply line to a rotating component, allowing the flow of media such as hydraulic fluid, compressed air, water, or coolant. This connection is maintained while the rotating part moves, ensuring that the fluid or gas is transferred smoothly without any leakage. Rotary unions are engineered to withstand high pressures, speeds, and temperatures, making them versatile components in manufacturing processes. It is widely used in metallurgy, engineering machinery, papermaking, chemical industry and other fields. Its core function is to ensure the efficient transmission of fluid media (hydraulic oil, steam, cooling water, etc.) in dynamic rotation scenarios while preventing leakage.
1. Basic concept
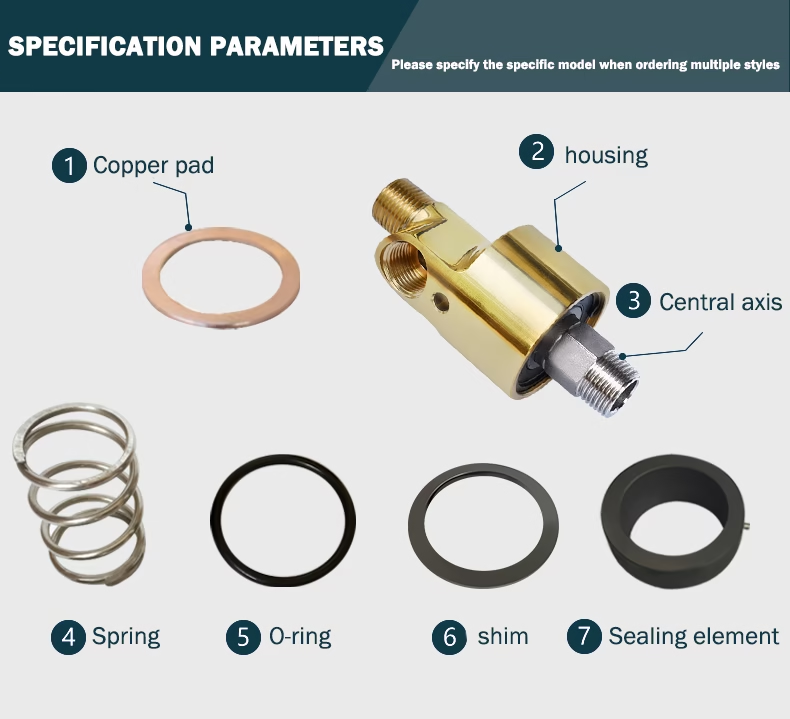
The rotary joint achieves dynamic sealing through internal seals. The key components include:
Sealing ring: Made of silicon carbide, metal-impregnated graphite and other materials, it is wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant.
Spring mechanism: Provides continuous compensation force to ensure the sealing surface fit.
Bearing: Supports rotating parts and balances radial/axial loads.

 The rotary joint is a common mechanical connection device used to achieve a rotary connection between two or more components. It usually consists of an inner ring, an outer ring, a ball and a retainer, etc., with a simple and reliable structure; the inner ring is fixed to the central axis of two adjacent components, and the outer ring is connected to another component. The inner ring and the outer ring are connected by balls and retainers. The balls are usually made of hard, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials such as steel or ceramics.
The rotary joint is a common mechanical connection device used to achieve a rotary connection between two or more components. It usually consists of an inner ring, an outer ring, a ball and a retainer, etc., with a simple and reliable structure; the inner ring is fixed to the central axis of two adjacent components, and the outer ring is connected to another component. The inner ring and the outer ring are connected by balls and retainers. The balls are usually made of hard, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials such as steel or ceramics.
They are placed in the groove between the inner and outer rings to form a rolling track, thereby reducing the friction between the contact points; the retainer is used to fix the position of the ball to prevent it from falling out of the groove. During operation, the rotary joint is lubricated by lubricant or grease to minimize the friction between the inner and outer rings, so that high-speed and smooth rotation can be achieved.
2.Medium transmission logic
Hydraulic oil: Transmitted through independent pipelines, supports high pressure (5000 psi) scenarios.
Steam/cooling water: Use siphon principle or inner tube design to ensure unidirectional flow of media.
High temperature media: Use double-layer seal + thermal conductive material to prevent thermal expansion leakage.
3. Dynamic sealing mechanism
Spring-assisted seal: Compensates for sealing surface wear and extends life.
Labyrinth seal: multi-layer structure blocks medium leakage (suitable for high temperature scenarios).
4. Mechanical seal structure
The dynamic ring and the static ring cooperate: the dynamic ring (hollow shaft) is pressed against the static ring by spring or fluid pressure to form a dynamic sealing surface to prevent medium leakage.
Function of elastic element: spring or bellows compensates for thermal expansion and wear to ensure continuous fit of the sealing surface.
Advantages of spherical seal design: Higher degree of freedom, adapting to equipment vibration and eccentricity (such as excavators, wind turbines).
How a Rotary Union Works
The working principle of different rotary union is different. The working principle of the rotary joint is to reduce the friction between the inner and outer rings by the rolling of the balls. When the two parts connected together, the relative movement between the inner and outer rings causes the balls to start rolling. Since the rolling friction of the balls is small, the friction between the contact points can reduce, thereby reducing energy loss and wear.
Lubricant or grease needs to inject into the rotary joint during operation to ensure good lubrication between the inner and outer rings. The lubricant can form a thin film between the inner and outer rings of the joint, reducing the contact area, thereby reducing friction and improving the rotation efficiency. In addition, the lubricant can also cool the joint to prevent overheating and damage.
High temperature rotary union
How a rotary union works? In the case of high temperature rotary joint through hot oil, if the rotary joint installed unilaterally, the 2 port hydraulic rotary union will be use. It can accessed simultaneously through a swivel joint. In order to uniform roll temperature, the installation of unilateral bidirectional rotary joint will generally use the inner tube for oil intake and the hole next to the shell will used as the oil outlet. The inner tube length is more than half of the roller. Drill some small holes into the tail section of the inner tube. In order to ensure that the oil inside the roller is full. It makes the inner tube bigger and the oil outlet smaller.
Steam swivel Joint
Steam swivel also called high temperature swivel joint. The difference is that the steam rotary joint is the side hole as the steam inlet. The inner tube acts as a siphon to drain water. The quality of drainage is directly related to the temperature of the roller. Therefore, the siphon generally uses a hard tube and a hose. The hard tube extends to the inside of the roller, and the hose droops close to the inner wall of the roller. In this way, the condensed water discharged under the pressure of the steam.
Water rotary union
How a water Rotary Union Works?The working principle of the water rotary joint is the same as that of the high temperature thermal oil rotary joint. The two-way rotary joint installed in one side. The water inlet speed is higher than the outlet speed. Keep the roller always full of water. If one installed at one end, it is best to enter the water quickly and the water slowly. However, because the water generally pressurized with a pump, the same rotary joint used at both ends of the same roller will also be fast water and slow water.
Single channel rotary union
How a rotary union works? Single-channel rotary joints mainly used in high-speed machine tools, printing, deep hole drilling, papermaking, semiconductors, steel mills and other industries. Its main working principle is that it can only rotate and transport a static medium source into a dynamic medium source. It cannot mix and transport multiple media. It mainly consists of two parts, one is a threaded rotor and the other is an anodized stator. The front section uses high-speed bearing support and a high-wear-resistant mechanical seal installed in the stator part. The bottom of the rotor made of alloy. The compression of the internal spring of the stator adjusted by the pressure of the medium to achieve a high-speed sealing effect.
The installation of the single-channel rotary joint adopts a threaded connection. The front rotor has a limiting boss for positioning and equipment installation concentricity. When the rotor thread twisted into the internal thread of the equipment, the concentricity needs to calibrat to ensure concentric installation. At the same time, the stator fixed and a soft connection method adopted. It can fix directly through the oil inlet pipe to ensure the stable and floating rotation of the single-channel rotary joint.
Multi-channel rotary union
How a rotary union works? There is a difference between the principles of multi-channel rotary joints and single-channel rotary joints. Multi-channel rotary joints refer to multiple channels that can mix and transmit multiple different types of media. They mainly pass the static medium source through the stator. Each ring of the stator and the rotor adopts a dynamic rotary seal. The medium enters from the stator and transported to the equipment parts through the rotor.
Multi-channel rotary joints widely used in automation equipment, turntable machinery, automatic drilling and tapping machines, hydraulic fixtures, engineering machinery, maritime, military industry, aerospace, steel mills and many other industries. The installation method is mainly to fix the rotor part on the rotating part of the equipment. There is a 2mm positioning boss on the upper end of the rotor flange, which used to locate the center of rotation of the equipment.
Special attention: it needs to installed at the center of rotation of the equipment. There are threaded holes on the rotor for connecting and fixing with the rotating parts of the equipment. There are also screw holes at the rear end of the stator part, which needs to fixe on the static parts of the equipment. At the same time, it should be note that the stator part cannot completely fixed, and a certain floating space required to ensure that when it rotates, it will rotate due to non-concentricity. This is the basic installation method of multi-channel rotary joints.
Selection Guide: 4-step precise matching
Determine the medium type: hydraulic oil/steam/cooling water, etc.
Calculate pressure and speed: match the seal grade and bearing type.
Select the connection form:
Flange connection: supports two-way rotation, suitable for high-precision equipment.
Threaded connection: Note that the direction of rotation is opposite to the direction of rotation (left-handed/right-handed).
Verify the installation method: Ensure that the coaxiality is <0.1mm to avoid eccentric wear.
Maintenance and care: the key to extending life
Daily inspection: clean the surface, monitor vibration, and lubricate regularly.
Troubleshooting:
Leakage: replace seals and check spring pressure.
Abnormal vibration: check bearing wear and recalibrate coaxiality.
Long-term out of use: drain the medium to prevent internal corrosion.
Conclusion
Rotary unions are indispensable components in modern machinery, facilitating the transfer of fluids and gases between stationary and rotating parts. Their ability to maintain leak-tight seals under various conditions makes them critical in industries ranging from aerospace to food processing. Understanding how rotary unions work and their applications can help engineers and technicians optimize their use, ensuring efficient and reliable operation of machinery.
By recognizing the importance of rotary unions and addressing potential challenges, industries can leverage these devices to improve productivity, reduce maintenance costs, and enhance overall system reliability. Whether in high-speed manufacturing processes or in critical aerospace applications, rotary unions play a vital role in ensuring continuous operation without interruption.
As technology advances, rotary unions are likely to see improvements in materials, design and functionality. Innovations in sealing technology and bearing systems will further enhance their performance and lifespan. Additionally, the integration of rotary unions with other technologies, such as automation and IoT, could lead to more efficient and intelligent systems.
How a rotary union works? In conclusion, rotary unions are not just simple mechanical devices; they are crucial components that enable the smooth operation of complex machinery across diverse industries. Their versatility, reliability, and ability to handle demanding conditions make them essential for modern manufacturing and technological advancements.