Coolant Rotary Unions: Ultimate Engineering Guide
In modern industrial equipment, efficient thermal management is critical. One often-overlooked but vital component in this chain is the coolant rotary union. This device enables coolant (liquid or gas) to pass from fixed infrastructure into rotating machinery without leakage or performance loss. When machines spin at high speeds or handle large thermal loads, a properly designed coolant rotary union becomes an essential element to maintain reliability, reduce downtime, and protect costly equipment.
Whether you are involved in manufacturing, plastics injection, wind‐power systems, or high-speed spindles, this guide will deliver a deep dive into coolant rotary unions — what they are, how they work, what design choices matter, and how to keep them running optimally.
Table of Contents
-
What is a Coolant Rotary Union?
-
Key Construction Materials
-
Base body
-
Seals & bearings
-
-
Typical Applications
-
CNC & machine tools
-
Wind turbines & renewable energy
-
Automotive test benches
-
Printing, lamination & plastics
-
-
Critical Technical Specifications
-
Media passages
-
Pressure & temperature ratings
-
Flow rate & rotational speed
-
Interface types
-
-
Performance Considerations
-
Thermal efficiency
-
Leakage control
-
Friction minimization
-
Maintenance interval
-
-
Varieties & Configurations
-
Single-pass vs multi-pass
-
Coaxial units
-
High-speed models
-
Corrosion-resistant / specialty units
-
-
How to Select the Right Union
-
Maintenance Best Practices
-
What Can Go Wrong: Failure Modes
-
Conclusion & FAQ
1. What is a Coolant Rotary Union?
Definition & Basic Functionality
A coolant rotary union, also known as a coolant swivel or rotary coupling, is a mechanical device designed to facilitate the transfer of coolant from a stationary source to a rotating component in machinery. Its primary function is to supply coolant, typically a liquid or gas, to moving parts, preventing overheating and ensuring optimal performance during operation.
These unions are designed to withstand high pressures and rotational speeds while maintaining a leak-free seal, which is essential for the longevity of both the union and the machinery it serves. Without a proper coolant rotary union, machinery can experience issues such as overheating, premature component wear, and reduced efficiency.
A rotary union is a mechanism that allows fluid to flow from a stationary supply (e.g., a coolant tank) into a rotating component (e.g., a spindle or drum). In coolant applications, its primary purpose is to:
Deliver lubrication and temperature control to cutting tools, bearings, or machinery parts.
Prevent leaks that could damage equipment, compromise safety, or increase operational costs.
Without rotary unions, systems like CNC lathes, printing presses, or wind turbines would face catastrophic failures due to overheating or friction.
In many industrial systems, rotating components generate heat via friction, high-speed operation, or heavy loads. Without effective cooling, internal temperatures rise, components expand, tolerances shift, and ultimately, failure or downtime may result. The coolant rotary union bridges the static and rotating parts by offering an internal fluid passage that rotates reliably, keeps sealing integrity, and manages flow under operational stresses.
In essence, it is not just a fitting or swivel – it’s a high-precision element designed to handle rotational motion, internal fluid flow, sealing, and dynamic forces simultaneously.
2. Key Construction Materials
Base Body Materials
The main housing or body of a coolant rotary union must resist pressure, mechanical loads, and often corrosive coolants or environments. Common materials include:
-
Brass: Good machinability and moderate corrosion resistance; often used in lower-pressure or less demanding applications.
-
Carbon Steel / Alloy Steel: Offers higher strength than brass and is economical; may require surface treatment or plating for corrosion protection.
-
Stainless Steel (e.g., 316 / 304): Excellent corrosion resistance, high strength; chosen when coolants are aggressive, or in hygienic/food/chemical environments.
-
Aluminum (in some lightweight applications): May be used when weight is critical and pressures are moderate, but is less common for heavy industrial cooling unions due to strength/corrosion trade-offs.
Seals & Bearing Materials
These internal components are critical for reliable performance. Seals prevent coolant escape; bearings enable smooth rotation. Material choices depend on coolant type, speed, temperature, pressure, and environmental factors:
-
Seal materials:
-
Fluoroelastomers (e.g., Viton) – high temperature and chemical resistance.
-
PTFE (Teflon) – very low friction, good chemical tolerance, ideal for high speed/low wear.
-
Nitrile (NBR) – cost-effective elastomer for moderate temperature and less aggressive fluids.
-
-
Bearing materials:
-
Hardened steel – widely used, good fatigue strength.
-
Stainless steel – for corrosive or hygiene applications.
-
Bronze or brass bushings – sometimes for lower speed, lower cost.
-
Ceramic bearings – for extreme speed or minimal lubrication regimes.
-
Choosing the right material combination is essential to ensure long life, minimal downtime, and reliable coolant transfer under harsh conditions.
3. Typical Applications
Coolant rotary unions are found across many industries. Here are some prominent examples:
CNC & Machine Tools
Rotating spindles on milling machines, lathes, or multi‐axis machining centres often require coolant to be delivered into high-speed rotating tooling. A well-designed rotary union ensures consistent flow into the spindle and prevents leakage or bearing damage.
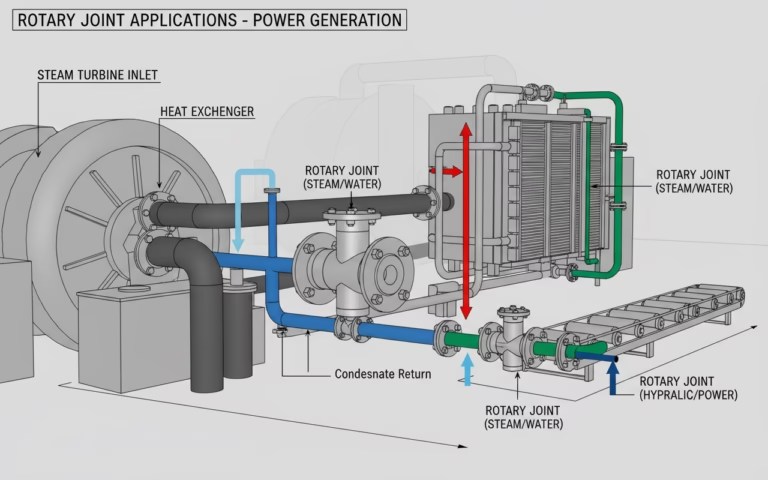
Wind Turbines & Renewable Energy
Large wind turbine nacelles house high-speed rotating generators and gearboxes that generate considerable heat. Cooler systems can integrate coolant rotary unions to channel fluid through the rotating parts, increasing efficiency and reducing wear.
Automotive Test Benches
In engine and drivetrain test rigs, rotating shafts must often be supplied with coolant to replicate operating conditions. The rotary union manages coolant input while allowing full rotation of the test device.
Printing / Lamination / Plastics Industry
Rollers, drums, and extruders in printing machines, laminators, or plastic injection machines often spin continuously and generate heat. Coolant rotary unions help maintain consistent roller temperature, improve product quality, reduce scrap, and avoid downtime.
Lathes
Lathes are another common application for coolant rotary unions. The coolant is used to cool the cutting tool and the workpiece during turning operations. A well-functioning rotary union for coolant in a lathe can improve the surface finish of the turned part, reduce the amount of heat generated during the cutting process, and increase the efficiency of the lathe operation.
Grinding Machines
Grinding machines generate a significant amount of heat during operation. Rotary unions for coolant are used to supply coolant to the grinding wheel and the workpiece. The coolant helps in dissipating the heat, preventing the workpiece from overheating and getting damaged, and also helps in flushing away the grinding debris. This results in a better-quality finish on the ground surface and extends the life of the grinding wheel.
In each of these settings, the coolant rotary union plays a crucial role in cooling, extending machinery life, and ensuring reliable high-volume production.
4. Critical Technical Specifications
When choosing a coolant rotary union, the following specifications are especially important:
Media Passages
How many separate flow channels are required? Single-pass units have one fluid path; multi-pass models offer multiple independent channels for different fluids or directions.
Pressure Rating
Define the maximum operating pressure the union will face. The device must be rated for the highest system pressure to avoid deformation or leakage.
Temperature Range
Operating temperature includes coolant inlet temperature, ambient environment, and potential temperature rise due to friction or high speed. The union must handle both fluid and mechanical thermal loads.
Flow Rate
Ensure the union can support the required volumetric flow of coolant without excessive pressure drop or flow disruption.
Connection Size & Type
Verify the union’s inlet and outlet thread size or flange type match the system. Mismatched connections can lead to installation issues or leaks.
Seal & Bearing Material
Choose materials compatible with the coolant chemistry, speed, temperature, and environment to avoid premature wear.
Rotational Speed (RPM)
High-speed applications impose greater demands on balancing, sealing, and bearing performance. The union must be rated for the RPM range of your system.
5. Performance Considerations
To maximise the performance of a coolant rotary union, engineers should focus on:
Thermal Efficiency
Delivering coolant effectively into the rotating part helps maintain temperature control, thereby improving accuracy, reducing scrap, and prolonging component life.
Leakage Control & Minimal Friction
Any leak represents wasted fluid, a potential environmental hazard, and may damage bearings. Minimising friction improves efficiency and longevity of the unit.
Seamless Operation
The union must reliably transfer coolant while the equipment rotates, without interruption, vibration, or excessive wear.
Compatibility & Low Maintenance
Materials, design, and assembly must match the application fluid, speed, and environment so that maintenance intervals are long and downtime is minimal.
6. Types of Rotary Unions for Coolant
✅Bearingless Unions
1117 series:
Deublin’s 1117 bearingless rotary union utilizes closed seal technology for long service life under harsh operating conditions. With bearingless unions, speed can range from 10,000 rpm up to 50,000 rpm. The elimination of bearings in this design reduces overall cost and allows for higher rotational speeds.
1121 series:
The bearingless 1121 rotary unions implement ppop-off®sealing technology. This unique feature allows the union to dry run even in the absence of media pressure. The short pop-off stroke limits coolant leakage when there is a tool change, making it ideal for applications where tool changes are frequent.
1124 series:
The 1124 full-flow design features balanced mechanical seals with patented auto sense® technology. This technology is a game-changer as it can sense if the media is coolant, MQL (Minimum Quantity Lubrication), or dry air and then respond by changing the seal operation accordingly. The bearingless rotating union is available with a threaded rotor only.
1139 series:
The 1139 bearingless, all-media rotary union features Deublin’s patented pop-off® seal technology. Pop-off seals remain closed when coolant is present, but allow a microscopic gap between the seals when pressure is removed. The non-rotating part of the union has a “stroke” to remain sealed when thermal expansion is caused by the spindle. This makes it suitable for applications where thermal expansion is a concern.
1154 series:
The 1154 auto sense rotary union automatically adjusts between sealing operations to accommodate different types of media. The long-stroke feature tracks drawbar movement, ensuring that the coolant supply remains consistent even when there are changes in the position of the drawbar.
1159 series:
Cool control technology in the 1159 series reduces coolant leaks when there is a tool change. An air pilot is used to keep the seals closed at the time of an axial drawbar movement. 1159 also contains autosense seal technology to adjust seals based on the media type, reducing seal wear and maintenance.
✅ Bore-Mounted Unions
Spindles with machined counter bores require a bore-mounted rotary union. The bore-mounted union features a channel that guides leakage through a drain line to prevent the spindle from flooding.
1109 series:
Deublin is also available in a bore-mounted design. Pop-off seal technology can run without media pressure, reducing early wear of seals. Pop-off rotary unions are best in through-spindle coolant applications.




1111 series:
Deublin’s bore-mounted rotary unions are designed for long-lasting service and ease of installation. They are engineered to fit perfectly into spindles with machined counterbores, providing a reliable coolant transfer solution.
1114 series:
Through-spindle coolant rotary unions, like the 1114 bore-mounted model, deliver media directly to the source to control overheating and increase productivity. It is easy to install and can handle up to 19mm of axial drawbar movement. Designed with autosense technology, the seals adjust based on the type of media.
✅ Rotor-Mounted Unions
Rotor-mounted unions attach directly to the machining center by the threaded rotor. The design makes for ease of installation and absorbs the thrust load on the spindle caused by coolant pressure.
1005 series:
Deublin’s bearing-supported, coolant rotary union is a single-piece design for ease of installation and replacement. Deublin offers two mounting styles, rotor and bore, to fit nearly all machining applications.






1101 series:
Deublin’s rotary union for coolant is designed with closed seal technology to reduce seal wear by remaining closed with or without the presence of media. The bearing-supported rotary union can absorb the spindle’s thrust load, reducing early wear.
1109 series:
Deublin’s popoff® design allows unlimited dry running without media pressure to prevent early seal wear. Pop-off rotary unions are best for machining that utilizes through-spindle coolant.
1114 series:
Deublin’s auto sense® sealing technology automatically senses the type of media and responds by adjusting the seal operation. This response provides higher feed rates and reduces unnecessary downtime. The threaded rotor is available in radial and axial connections with ease of installation.
✅ Multi-Passage Unions
A multi-passage rotating union requires balanced mechanical seals to handle high speeds and reduce the wear of the union. Deublin’s standard line of multi-passage rotary unions can meet a variety of application needs, including workholding requirements with 1 to 8 channels.
2620 series:
When transferring two types of media, Deublin’s multi-passage 2620 contains two independent passages with balanced mechanical seals. The seal design enables maximum operation and an extended lifespan. The two-passage rotary union is recommended for applications such as machine tool spindles, diaphragm chucks, or clamping and unclamping.

2630 – 2650 series:
The multi-passage rotary union contains 3 to 5 independent passages for different types of media, including coolant and dry air. Balanced mechanical seals are integrated with autosense technology to withstand high speeds and pressures. The 2630 is a powerful solution for clamping, tool sensing, and spindle cooling.
2606 – 2608 series:
Best suited for data-driven rotary tables, the multi-passenger high-speed rotary union can have up to 8 media channels for various media. Closed-seal technology keeps passages independent, restricting media from mixing without leakage.
1379 – 1479 series:
Designed with four independent passages, Deublin’s 1379 and 1479 rotary unions operate with various types of media, such as hydraulic oil. A vent between passages eliminates cross-contamination of two types of media. The four-passage rotary union is best for applications like clamping, unclamping, and more.
7. How to Select the Right Union
Here is a streamlined selection process:
-
Define your rotational system: speed, load, direction, and mounting constraints.
-
Specify your cooling circuit: coolant type, flow rate, pressure, and temperature range.
-
Match the number of passages & connection types.
-
Evaluate environmental and chemical conditions—material compatibility is vital.
-
Choose a union rated for your maximum design limits (pressure, temp, RPM) with a margin.
-
If in doubt or for complex applications, engage with a rotary union manufacturer or engineering specialist to optimise.
8. Maintenance Best Practices
Routine upkeep dramatically extends service life:
-
Inspection: Regularly check for leaks, abnormal noises, or heat build-up.
-
Lubrication: Follow manufacturer guidelines if bearings require lubrication.
-
Seal Replacement: Monitor seals for wear or degradation and replace before failure.
-
Cleaning & Flush: Clean fluid paths and remove contamination.
-
Alignment & Balance: Particularly in high-speed drives, ensure the union and rotating component remain aligned and balanced to reduce stress.
-
Record-Keeping: Maintain logs of installation, service, fluid changes, and inspection results.
Proactive maintenance reduces unplanned downtime, improves reliability, and extends machine life.
9. What Can Go Wrong: Failure Modes
Even well-designed units can fail if conditions are not managed:
-
Insufficient lubrication leads to bearing failure and heat build-up.
-
Improper installation (misalignment, incorrect connection) causes stress and seal damage.
-
Seal wear or failure leads to fluid leakage, contamination ingress, or pressure loss.
-
Exceeding rated limits (speed, pressure, temperature) causes structural failure, excessive wear, or sudden breakdown.
-
Contamination (particles, debris, aggressive fluid) causes erosion, blockage, and accelerated wear.
-
Lack of maintenance allows small problems to escalate into major failures.
-
Incorrect use—using the unit in an application beyond its design parameters—can lead to early failure.
Understanding these modes aids in diagnostics and preventive planning.
10. Conclusion & FAQ
In summary, coolant rotary unions are indispensable components in many rotating-machine cooling systems. With the right design, materials, configuration, and maintenance, they help deliver efficient cooling, extend machine life, and keep production running smoothly. When selecting a unit, pay attention not only to nominal specs but to how they align with your specific conditions — speed, pressure, coolant chemistry, environment.
FAQ
Q1: What’s the primary purpose of a coolant rotary union?
A: To transfer coolant from a stationary system to a rotating component, ensuring continuous flow in dynamic applications.
Q2: Can any coolant fluid be used with a rotary union?
A: Not necessarily — you must consider fluid chemistry, temperature, pressure, and compatibility with the union’s seals and materials.
Q3: How frequently should maintenance be done?
A: Frequency depends on load and environment, but at a minimum, plan periodic inspections, lubrication/seal checks, and cleaning – follow the manufacturer’s guidelines.