What is a Rotary Joint? A Complete Guide to Definition, Types, Applications and Benifits
Core definition and technical analysis
1. Definition of rotary joint
Someone asked me: Why do we need to use a rotary joint? What exactly is a rotary joint? Put. A rotary joint is a connector for transporting media between a static pipeline and a dynamic pipeline. The same is true in reverse. It is a connector for transporting media from a dynamic pipeline to a static pipeline. The medium can be air, other gases, liquids, steam, particles, etc. Therefore, a rotary joint is a precision sealing connection device used to transmit fluid media (liquid, gas, or steam) between a static pipeline and a rotating device, achieving leakage-free transportation under 360° continuous rotation.
The choice depends on the use and the type of fluid being moved. It fits well with the customer’s equipment. It has a compact design structure and adopts a flange connection. Even if the connected parts move relative to each other, it ensures that the fluid flows smoothly and continuously.
Manufacturers usually make it from steel, stainless steel, or brass. The choice depends on the use and the type of fluid being moved. It fits well with the customer’s equipment. It can rotate the pipe without harming it.
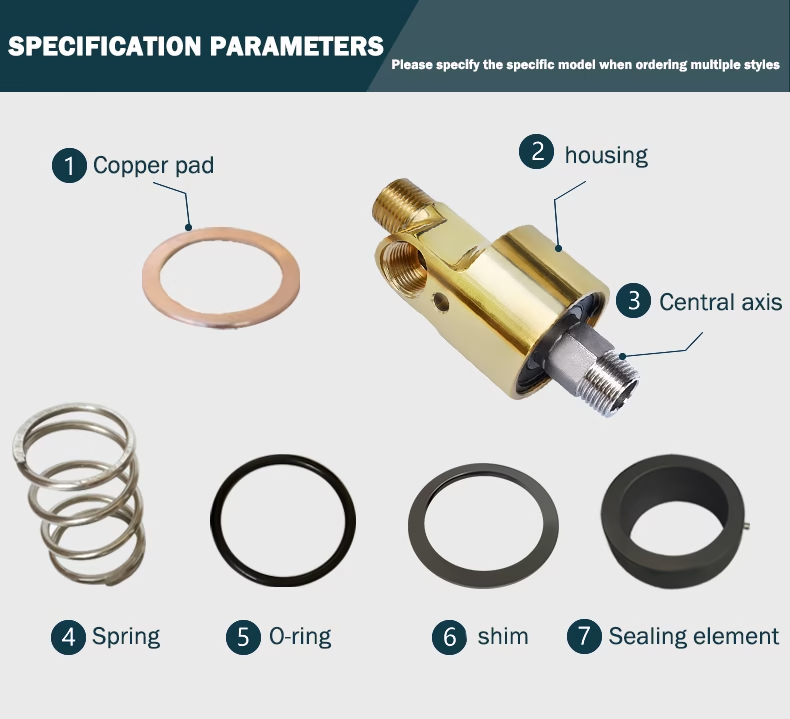
2. Structure of rotary joint
A rotary joint mainly consists of three parts: outer shell, axis, sealing parts, and bearing.
🔩 Shell
Function: Fixed part, connected to the fluid supply.
Material: Steel, stainless steel, brass (select according to application and fluid type).
🔄 Axis
Function: Rotating part, connected to rotating equipment such as rollers, rollers or spindles.
Material: Steel or stainless steel, wear-resistant and durable.
🛡️ Seals
Function: Prevent fluid leakage between the fixed shell and the rotating shaft. Pressure, temperature, and friction resistance are required.
Types
Lip Seal: Simple and effective, often used in low-pressure applications.
Mechanical Seal: Provide a more robust seal for high-pressure and high-speed applications.
Packing Seal: made of woven or molded material, adjustable for a tighter seal.
O-ring: Used with other seals to provide additional sealing.
Material: Typically made of elastomers like NBR (nitrile), FKM (fluoro rubber), or PTFE (Teflon). The choice depends on the fluid and operating conditions.
⚙️ Bearing
Function: Supports rotating shafts to ensure smooth, low-friction operation and reduce fatigue.
Types:
Ball Bearing: Suitable for light loads and high speeds.
Roller Bearing: Suitable for heavy loads and more durable.
Plain Bearing: Suitable for slow speeds, economical and practical.
Materials: Steel, bronze, ceramic, or plastic for special applications.
3. Working principle
The rotary joint operates based on the working principle of the bearing. It installs a bearing between the inner ring and the outer ring.
The sensor connects to the inner ring as the output end, and the drive device connects to the outer ring as the input end. The input end of the rotary joint changes rotary drive motion into axial thrust. It creates friction between the inner and outer rings through the bearing. This joint also sends the right rotary motion to the output end. It transmits torque and rotary motion between the inner and outer rings.
Types of Rotary Joints
There are many opinions on the types of rotary joints in the market, and there is no unified standard. Experts usually classify the common types based on key factors. These factors include fluid medium, sealing type, medium temperature, working pressure, rotation speed, and number of channels.
1. By fluid media
💧 Water Rotary Joints
✔️ Suitable for cooling systems and cleaning equipment
✔️ Corrosion-resistant, strong sealing
🔥 Thermal Oil Rotary Joint
✔️ Designed for high-temperature thermal oil transmission
✔️ Suitable for heating rollers and drying equipment
💨 Steam Rotary Joints
✔️ High-pressure resistance and high-temperature resistance
✔️ Commonly used in the papermaking and textile industries
⚙️ Hydraulic Rotary Joints
✔️ Transmit high-pressure hydraulic oil
✔️ Precision control of industrial machinery movement
🌬️ Compressed Air Rotary Joint
✔️ Realize 360° free rotation of pneumatic equipment
✔️ Suitable for automated assembly lines and packaging equipment
2. By connection channels
It can be divided into: single-channel rotary joint, dual-channel rotary joint, and multi-channel rotary joint. Multi-channel rotary joints are generally rotary joints with more than three channels.
3. By sealing forms
It can be divided into: ring seal rotary joint, mechanical seal rotary joint, and gap seal rotary joint. Many factors affect how the seal type rotates. These include the medium temperature, pressure, and the rotary joint’s rotation speed.
4. By pressures
It can be divided into: negative pressure, low pressure, medium pressure, and high pressure rotary joints. Under normal circumstances, such as vacuuming, rotary joints need to be able to withstand negative pressure; our common heating and cooling industrial equipment usually only needs to withstand low pressure, and the fluid circulates due to the inlet and outlet; and hydraulic equipment needs to withstand certain medium and high pressures because of the large torque so that the hydraulic equipment can operate normally.
5. By different temperatures of the fluid medium
It can be divided into: normal temperature rotary joints, high temperature rotary joints, and low temperature rotary joints. The fluid will go through different media based on its needs. This can include heating, cooling, or cleaning. In addition, some high-pressure rotary joints will heat up when the seal reaches a certain speed, and the design requires the rotary joints to withstand a certain high temperature.
6. By different speeds of the equipment
It is usually divided into low-speed, medium-speed, and high-speed rotary joints. According to the speed requirements of the rotating equipment, we must fully consider the rotation speed working requirements that the rotary joint cannot adapt to.
How to Choose the Right Rotary Joint
1. Core Parameter Comparison Table
🔧 Industrial Grade
Speed: < 5000 RPM
Pressure: < 20 MPa
Temperature: -40 ~ 200 ℃
🎯 Precision Grade
Speed: < 10000 RPM
Pressure: < 5 MPa
Temperature: -196 ~ 800 ℃
🚀 Extreme Environment
Speed: > 20000 RPM
Pressure: > 100 MPa
Temperature: > 1000 ℃
2. Selection Decision Tree
💧 Media Type
Applicable media: oil, water, gas, or electricity.
🔥 Pressure/ Temperature
Please check the operating level; Example: 300°C, 3000 psi.
⚙️ Speed Requirement
RPM Requirement: Example: 500 RPM vs. 10,000 RPM.
Applications of Rotary Joints
1. Machine Tools
✅ Coolant Delivery:
Lathes: Coolant is supplied through rotary joints to cool the cutting tool and workpiece during machining.
Milling Machines: Facilitates coolant flow to the cutting area, reducing heat buildup and improving tool life.
Grinding Machines: Ensures continuous coolant supply to the grinding wheel and workpiece interface.
Hydraulic Systems: Transfers hydraulic fluids to power tools and actuators within machine tools.
2. Printing Presses
✅ Ink Transfer:
Provides ink to the printing cylinders while allowing them to rotate freely.
✅ Water Management:
Delivers water to dampening systems to control moisture levels on the printing plates, ensuring high-quality prints.
3. Plastic Injection Molding
✅ Coolant Circulation:
Supplies coolant to molds for temperature control, ensuring consistent product quality and faster cycle times.
Maintains optimal mold temperature to prevent defects such as warping or shrinkage.
4. Textile Machinery
✅ Dyeing Machines:
Facilitates the transfer of dye solutions to the rotating drums or cylinders used for fabric dyeing.
✅ Finishing Equipment:
Ensures precise water flow control for washing, rinsing, and finishing processes in textile manufacturing.
5. Packaging Equipment
✅ Labeling and Sealing:
Provides adhesive or sealing material to labeling heads and sealing stations.
Ensures efficient fluid transfer for hot melt adhesives and other materials.
6. Paper Manufacturing
✅ Press Section:
Delivers steam or hot water to the press section for drying purposes.
✅ Calendar Rolls:
Provides heated oil or steam to calender rolls for maintaining the desired paper smoothness and thickness.
✅ Coating Machines:
Transfers coating fluids to the coating applicator rolls, ensuring uniform application.
7. Robotics and Automation
✅ Fluid Supply:
Integrated into robotic arms to supply air, hydraulic fluid, or coolant to end-effectors.
Enables complex movements while maintaining fluid connectivity.
8. Hydraulic Machinery
✅ Hydraulic Fluid Transfer:
Facilitates the transfer of hydraulic oil between stationary and rotating parts of hydraulic machinery.
Commonly used in construction equipment, agricultural machinery, and industrial robots.
9. Food Processing
✅ Washing and Rinsing:
Supplies clean water for washing and rinsing machines for fruits, vegetables, and other food products.
✅ Sanitization:
Ensures proper distribution of sanitizing fluids to maintain hygiene standards.
✅ Pasteurization:
Provides steam or hot water for pasteurization processes, ensuring food safety.
10. Medical Devices
✅ Sterile Fluid Transfer:
Used in medical devices requiring sterile fluid transfer, such as dialysis machines and diagnostic equipment.
✅ Temperature Control:
Maintains controlled temperatures in medical instruments and devices.
11. Agricultural Equipment
✅ Irrigation Systems:
Supplies water to rotating sprinkler heads or irrigation arms.
✅ Spraying Equipment:
Facilitates the transfer of pesticides and fertilizers to spraying nozzles on agricultural machinery.
12. Wind Energy
✅ Pitch Control Systems:
Transfers hydraulic fluid or electrical signals to pitch control mechanisms in wind turbines.
✅ Yaw Control Systems:
Ensures reliable fluid transfer for yaw control systems that orient the turbine blades towards the wind direction.
13. Steel and Metal Industry
✅ Rolling Mills:
Provides coolant to rolling mill rolls to reduce friction and heat during metal forming processes.
✅ Heat Treatment Furnaces:
Supplies cooling fluids to heat treatment furnaces for controlled cooling of metals.
14. Automotive Manufacturing
✅ Painting Booths:
Supplies paint and solvent to rotating painting heads or robotic arms.
✅ Assembly Lines:
Ensures efficient fluid transfer for various assembly line operations, including lubrication and cleaning.
15. Oil and Gas Industry
✅ Drilling Equipment:
Transfers drilling mud and other fluids to the drill bit during drilling operations.
✅ Refining Processes:
Facilitates the transfer of chemicals and fluids in refining processes, ensuring safe and efficient operation.
16. Marine and Shipbuilding
✅ Propulsion Systems:
Transfers hydraulic fluid to steering gears and propulsion systems.
✅ Cooling Systems:
Supplies seawater or coolant to engine cooling systems and other onboard machinery.
17. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
✅ Process Equipment:
Ensures sterile fluid transfer in pharmaceutical process equipment, including reactors and mixers.
✅ Filtration Systems:
Provides necessary fluids for filtration and purification processes. In short, the rotary joint is a very important mechanical element that can realize the rotation and movement of pipelines and meet the needs of various industrial equipment. In the future, with the continuous development of industrial technology, the application field of rotary joints will be more extensive.
Benefits of Rotary Joints
As a key mechanical component, the rotary joint plays an important role in industrial equipment. Its advantages are reflected in many aspects, which are explained in detail below:
1. Excellent sealing performance
Prevent leakage: Use special materials and structures (such as silicon carbide seals and labyrinth seal design) to ensure no leakage during the transportation of high-pressure, high-temperature, or corrosive media, and improve equipment safety.
Adapt to complex environments: The sealing ring consists of corrosion-resistant and high-temperature resistant materials that maintain stable sealing under harsh working conditions to prevent leakage of media or intrusion of external impurities.
2. Long life and low maintenance cost
Wear-resistant materials: Key components are made of high-strength stainless steel, nitrided steel, etc., to reduce friction loss and extend service life.
The design allows for easy maintenance: You can judge the wear of the seal by its visual appearance, which makes timely replacement convenient. Some structures support quick disassembly and assembly to reduce downtime.
3. Improve equipment operation efficiency
Efficient transmission: Precision bearing design (such as angular contact ball bearings) ensures flexible and smooth rotation and reduces energy loss.
Reduce the failure rate: Optimize the seal and structure to avoid equipment failure caused by medium leakage and improve overall operation stability.
4. Flexible equipment connection and motion conversion
Multi-channel design: supports single and dual-circuit structures. This meets the transmission needs of different media like water, steam, oil, and air.
Motion form conversion can change rotary motion into linear motion or the other way around. This helps meet the needs of complex mechanical systems.
5. Energy saving and environmental protection
Reduce resource waste: prevent medium leakage, and avoid energy (such as steam, cooling water) and material waste.
The design reduces noise and vibration.
It uses an elastic diaphragm for pre-stressing.
This improvement makes the work area more pleasant.
6. Wide applicability and customization
Multi-field application: covers multiple industries such as chemical, petroleum, metallurgy, papermaking, food, etc., to meet the connection needs of different equipment.
We can offer customized solutions. This includes special rotary joints for high temperature, high pressure, and high-speed needs. We create these solutions based on several factors. These include the characteristics of the medium, like temperature, pressure, and corrosiveness. We also consider the speed of the equipment.
7. Reduce long-term operating costs
Reduce downtime: A high-reliability design reduces failure frequency and shortens the maintenance cycle.
Save on replacement costs: You can replace seals one at a time when they wear out. This way, you don’t have to replace all the equipment, which lowers maintenance costs.
Installation Tips for Rotary Joints
1. Handling and Storage
Avoid collision and falling of rotary joints during transportation and storage to avoid damage to the interface and internal parts.
2. Installation Alignment
Install the machine concentrically as much as possible to ensure the good operation of the rotary joint.
3. Thread Direction Check
When installing the threaded rotary joint, pay attention to whether the thread direction of the inner and outer tubes corresponds to the rotation direction of the drum, and the thread rotation direction of the inner and outer tubes should also be consistent.
4. Flexible Connection Required
The connection between the rotary joint and the pipeline must be connected with a hose (it is recommended to use a flexible metal hose), and a rigid connection is prohibited.
5. Hose Positioning
The inlet and outlet of the rotary joint should be directly connected to the hose as much as possible. To reduce the auxiliary weight of the joint and extend the service life.
6. Inner Tube Assembly
When assembling the inner tube, pay attention to the size matching and weight auxiliary support. It is recommended to use the tolerance matching of H8/e7 for the matching of the inner tube and the joint of the internal rotating rotary joint.
7. Support and Anti-Rotation Clearance
The support and anti-rotation of the rotary joint should be appropriate. Generally, the rod diameter should be 2mm smaller than the anti-rotation hole to avoid affecting the free adjustment and compensation of the rotary joint.
Maintenance and troubleshooting
Maintaining rotary joints is important. This includes regularly replacing seals, lubricating bearings, and cleaning out dirt. These steps help ensure they work well and last longer. Proper maintenance can not only improve the operating efficiency of mechanical equipment but also reduce the failure rate.
🔄 Regular Replacement of Seals
Replace seals regularly
Wear of seals is the main cause of leakage.
Regular replacement ensures tight connections and prevents leakage.
🛢️ Lubrication of Bearings
Regular lubrication of bearings
Lubrication is the key to keeping the swivel running smoothly.
Regularly replenishing lubricants can effectively reduce friction and wear.
🧹 Cleaning Internal Impurities
Removing internal impurities
Impurities are easily accumulated during use.
Regular cleaning prevents blockage and ensures stable performance.
✅ Tips
Good daily maintenance can significantly extend the service life of the swivel joint and reduce the risk of failure.
Common Challenges & Solutions
🔧 Leakage
Cause: Seal wear
Fix: Regular maintenance
Use high-quality sealing materials (such as PTFE).
🔥 Heat Buildup
Cause: High-frequency and high-speed operation
Fix: Integrated cooling channels
Use heat-resistant alloy materials
🛡️ Material Compatibility
Cause: Corrosion or material mismatch
Fix: Use stainless steel or ceramic parts to prevent corrosion.
Conclusion
Rotary joints are the backbone of modern automation, enabling everything from wind energy to precision manufacturing. Whether you’re upgrading machinery or designing a new system, understanding rotary joints ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Do you need a Rotary Joint? Contact our experts for tailored solutions!







Any problems, kindly contact us via email: dannhydraulic@gmail.com
Kindly read this blog: https://dannhydraulic.com/what-is-rotary-joint/.