Application and performance analysis of high temperature rotary joints in coating machines
Introduction
With the rapid progress of modern industrial technology, coating machines have become indispensable in a variety of advanced industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, optical lens production, solar cell fabrication, and decorative coating applications. These systems deposit one or more thin layers of material on a substrate through physical or chemical methods, enhancing its optical, electrical, mechanical, or chemical properties. During this delicate process, high temperature rotary joints play a crucial yet often overlooked role. Acting as precision components that connect rotating parts to stationary fluid lines, they ensure reliable transmission of heat transfer media—such as cooling water, thermal oil, or compressed gas—under extreme temperature and rotational conditions. The performance of these joints directly influences the stability, productivity, and coating quality of the entire system.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of the applications, performance characteristics, selection principles, and future trends of high temperature rotary joints in coating machines, helping engineers and procurement specialists better understand their value in high-precision manufacturing.
1. Basic Function and Working Principle of High Temperature Rotary Joints
A high temperature rotary joint (also known as a high temperature rotary union) is a precision mechanical device designed to transfer fluid or gas between stationary and rotating components without leakage, even under high-speed and high-temperature conditions.
In coating machines, rotary joints are commonly installed at rotating cathodes, substrate carriers, or heating assemblies. They allow continuous and stable delivery of cooling or heating media, ensuring that the rotating elements remain within safe thermal limits. Without such a system, excessive heat could cause deformation, reduced coating uniformity, or even catastrophic equipment failure.
The core working principle relies on dynamic sealing technology. The sealing interface—comprising precision-engineered rings and high-temperature-resistant seals—maintains tight contact during rotation, preventing any leakage of process media. Advanced designs incorporate balanced mechanical seals, self-lubricating bearings, and anti-friction coatings to minimize wear and maintain performance even when operating above 400°C.
For example, in magnetron sputtering systems, high temperature rotary joints are often connected between the rotating target and the cooling circuit. They ensure effective heat removal during the sputtering process, preventing thermal stress that could damage the target or reduce coating uniformity.
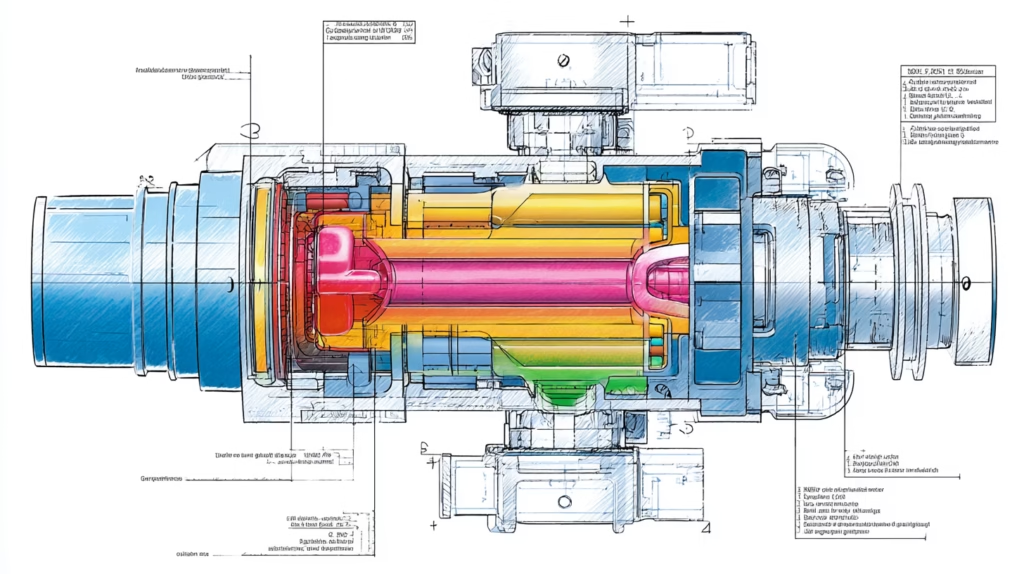 2. Applications of High Temperature Rotary Joints in Coating Machines
2. Applications of High Temperature Rotary Joints in Coating Machines
2.1 Rotary Cathode Systems
In magnetron sputtering coating equipment, rotary cathodes operate continuously at high power, generating significant heat. High temperature rotary joints circulate cooling water through the rotating cathode body, efficiently removing excess heat. This enables stable sputtering rates and prolonged target life.
The rotary motion, made possible by the joint, ensures uniform target erosion, improving both material utilization and film thickness uniformity. As a result, these rotary unions are essential for maintaining consistent coating performance in large-area or high-rate deposition systems.
2.2 Heating Systems and Substrate Holders
Certain coating processes—such as Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD)—require substrate temperatures reaching several hundred degrees Celsius. In these cases, high temperature rotary joints connect rotating substrate holders to the heating system, allowing for the transfer of hot oil, steam, or electric current while maintaining smooth rotational motion.
This design ensures uniform heating across the substrate, which is critical for achieving even film deposition and avoiding coating defects. In addition, the use of multi-passage rotary joints allows simultaneous transmission of different media, such as heat transfer oil and process gas, within a compact assembly.
2.3 Vacuum Chamber and Drive Systems
In high-end vacuum coating equipment, certain internal components—such as rotary feedthroughs or transfer shafts—must operate under both vacuum and elevated temperatures. High temperature rotary joints make it possible to deliver cooling media or drive torque through these sealed environments, ensuring continuous and reliable operation of moving parts within the vacuum chamber.
The use of vacuum-compatible materials, such as stainless steel, high-purity graphite, and ceramic seals, prevents outgassing and maintains ultra-high vacuum conditions essential for precise coating quality.
3. Performance Advantages of High Temperature Rotary Joints
3.1 Exceptional Heat Resistance
Standard rotary joints often fail under extreme temperatures due to seal degradation or thermal expansion. In contrast, high temperature rotary joints are constructed from advanced materials like technical ceramics, high-purity graphite, and heat-resistant alloys (e.g., Inconel or stainless steel SS316). These materials maintain mechanical integrity at temperatures exceeding 400°C, making them ideal for continuous operation in coating environments.
Special sealing elements, such as perfluoroelastomer (FFKM) or graphite composite seals, ensure leak-free performance without hardening or cracking even after prolonged exposure to heat.
3.2 Excellent Wear Resistance and Extended Service Life
Coating machines often operate under continuous, high-speed rotation, which subjects rotary seals to significant friction and wear. To address this, manufacturers employ surface hardening treatments, ceramic coatings, and self-lubricating designs to minimize mechanical abrasion.
For instance, rotary joints featuring silicon carbide (SiC) sealing rings can deliver service lives several times longer than those with standard materials. The combination of wear-resistant design and proper lubrication results in long-term reliability and lower maintenance costs.
3.3 High-Precision Sealing Performance
In vacuum coating processes, even minimal leakage can compromise vacuum levels or contaminate process gases, leading to coating defects. High temperature rotary joints adopt multi-stage sealing systems and ultra-precise machining tolerances to maintain sealing integrity even during rapid temperature fluctuations or dynamic loading.
This superior sealing capability makes them suitable for high-vacuum or ultra-high-vacuum systems, where purity and pressure control are critical.
3.4 Compact Design and Easy Integration
Modern coating machines prioritize compact layouts and modular designs. To meet this demand, high temperature rotary joints are engineered with space-saving dimensions and standardized interfaces. Their compact form allows seamless integration into tight equipment assemblies without compromising performance.
Additionally, modular connection ports simplify installation, replacement, and maintenance, reducing equipment downtime and improving operational efficiency.
3.5 Media Compatibility and Multifunctionality
One of the most versatile advantages of high temperature rotary joints lies in their ability to handle a wide range of media, including deionized water, thermal oil, compressed air, inert gases, and even vacuum process gases.
Advanced multi-channel rotary joints can simultaneously transfer multiple fluids and electrical signals through independent, sealed passages—ideal for complex coating processes involving cooling, heating, and control systems.
4. Selection and Maintenance Guidelines
4.1 Key Selection Parameters
Choosing the correct high temperature rotary joint requires careful consideration of the following factors:
-
Operating Temperature and Pressure: Select materials and seals rated for the maximum expected conditions to ensure stable performance under extreme environments.
-
Fluid Type: Choose materials compatible with the process medium—water, oil, or gas—to prevent corrosion or contamination.
-
Rotational Speed and Torque: Ensure the joint design supports the equipment’s speed and mechanical load without excessive wear.
-
Vacuum Compatibility: For vacuum applications, use low-outgassing materials and seals.
-
Certifications and Quality Standards: Prioritize products certified under ISO 9001, CE, or other industrial standards to guarantee reliability and safety.
4.2 Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
To maximize service life and maintain peak performance:
-
Follow installation manuals carefully. Ensure the sealing surfaces are clean and properly aligned before tightening.
-
Inspect periodically. After every 500–1000 hours of operation, check the seal condition and replace worn parts if necessary.
-
Filter the medium. Install a fine filter in the cooling or heating circuit to prevent solid particles from damaging the seals.
-
Monitor operating parameters. Record temperature, pressure, and vibration data to detect potential problems early.
-
Use proper torque settings. Avoid over-tightening, which can distort the sealing interface.
Proper maintenance not only extends the lifespan of the rotary joint but also prevents costly downtime in precision coating operations.
5. Market Overview and Development Trends
The global market for high temperature rotary joints is currently dominated by manufacturers from Europe, the United States, and Japan, including companies such as Deublin (Germany), Rotary Systems Inc. (USA), and Higaki Sangyo (Japan). These firms offer high-performance rotary unions widely adopted in the semiconductor and vacuum coating industries.
However, Chinese manufacturers and research institutes are rapidly advancing their technological capabilities. With improved material processing, machining precision, and quality control, domestic brands are closing the gap with international competitors—offering reliable, cost-effective alternatives for global buyers.
Looking forward, the next generation of high temperature rotary joints will evolve toward:
-
Smart Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance: Integrated sensors will continuously track temperature, pressure, and wear conditions, enabling early fault detection and real-time performance diagnostics.
-
Material Innovation: Advanced nanocoatings and ceramic-matrix composites will enhance thermal stability, wear resistance, and chemical durability.
-
Customized Engineering Solutions: Manufacturers will offer tailor-made rotary unions for specific coating processes such as PVD, CVD, or ALD, ensuring optimal compatibility with different coating environments.
-
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: Future designs will focus on reducing energy losses and improving cooling efficiency to meet environmental and operational demands.
Conclusion
Although high temperature rotary joints may appear as auxiliary components in coating machines, their importance cannot be overstated. These precision-engineered devices ensure reliable heat management, consistent rotation, and leak-free operation—all of which are critical for achieving high-quality coating results.
Their superior thermal resistance, wear durability, and sealing accuracy form the backbone of stable coating performance in demanding industrial environments. As coating technology continues to advance toward higher precision and automation, innovations in rotary joint design will remain a key driving force behind the evolution of the industry.
For engineers, maintenance teams, and procurement professionals, selecting the right rotary joint—supported by proper installation, monitoring, and preventive maintenance—will significantly enhance system performance and extend equipment life, ensuring maximum return on investment.







