How pneumatic rotary union work?
Pneumatic rotary union plays an essential role in modern industrial automation, enabling compressed air to transfer reliably between stationary and rotating components. From packaging machinery to robotics, CNC systems, and printing equipment, these precision-engineered devices ensure continuous airflow without leakage or performance loss.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down how pneumatic rotary unions work, their internal components, common design variations, applications, benefits, and key selection factors. This article is optimized for SEO and engineered for engineers, procurement specialists, and technical teams who need detailed, authoritative information.
What Are Pneumatic Rotary Unions?
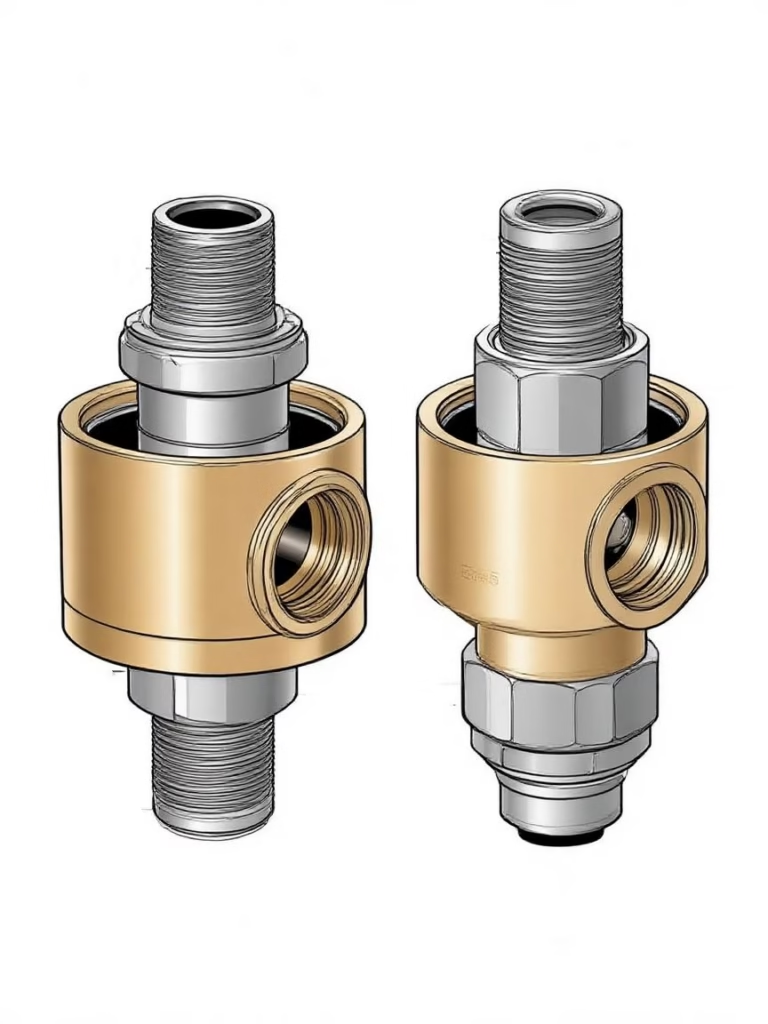
A pneumatic rotary union is a mechanical coupling that maintains a leak-proof connection while enabling rotational motion between two interconnected parts. Unlike hydraulic rotary unions designed for liquids, pneumatic versions specialize in transferring compressed air or gases (e.g., nitrogen, CO₂) in systems requiring continuous 360° rotation.
The pneumatic rotary union is a rotary connector driven by air pressure, which is mainly composed of a rotating part and a fixed part. The rotating part includes the rotor and the bearing under the rotor, and the fixed part includes the stator and the sealing ring above the stator. The structure of the rotor and the stator is relatively simple. Usually, there is a gas flow channel on the rotor, and after the gas enters the channel from the gas source, the movement of the rotor is driven by pressure, and then the rotation of the rotor is realized, to achieve the role of rotary connection.
Unlike hydraulic rotary unions designed for fluids at high pressure, pneumatic rotary unions handle air systems with lower pressure but require extremely precise sealing to prevent leakage or pressure drop.
How Pneumatic Rotary Unions Work: The Core Mechanism
To understand the working principle, it helps to examine the two main functions of a pneumatic rotary union:
- Enable continuous 360° rotation
-
Maintain airtight sealing during air transfer
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how the mechanism works.
1. Air Enters Through the Stationary Side
Compressed air from the supply line enters the stationary inlet port of the rotary union. Depending on the design, the inlet may be:
-
Threaded (NPT, BSP, BSPT)
-
Flanged
-
Quick-connect type
The stationary housing remains fixed and does not rotate. It distributes the incoming airflow into the internal passage.
2. The Shaft or Rotor Rotates Independently
Inside the union, the rotor (or shaft) is connected to the rotating machinery component. While the housing stays still, the shaft rotates freely, supported by precision bearings.
High-quality pneumatic rotary unions are used:
-
Ball bearings (for low torque applications)
-
Roller bearings (for higher load conditions)
-
Hybrid ceramic bearings (for high-speed rotational performance)
These bearings ensure smooth, low-friction rotation while preventing misalignment.
3. Sealing System Maintains Airtight Transfer
Sealing is the most crucial aspect of pneumatic rotary union design. Because air is compressible, even minor gaps can cause leaks or pressure drops.
Common sealing types include:
a. Mechanical seals
-
Excellent sealing performance
-
Suitable for high-pressure air systems
-
Long lifespan with proper lubrication
b. Lip seals
-
Low friction
-
Ideal for low-pressure, high-speed rotation
c. O-ring seals
-
Used for internal chamber separation and leakage protection
-
Provide a cost-effective sealing solution
The seals maintain constant contact between the stationary housing and the rotating shaft, ensuring an airtight flow path.
4. Air Flows Through Internal Passageways
Once the air passes the sealing system, it enters the internal passage inside the rotating shaft. Pneumatic rotary unions may have:
-
Single passage → one air channel
-
Dual passage → separate chambers for supply and return air
-
Multi-passage → multiple air circuits for complex automation systems
Multi-passage pneumatic unions require precise chamber separation to avoid cross-contamination.
5. Air Exits Through the Rotating Side
The air then exits the rotating outlet of the union and travels into the rotating component—such as a rotary actuator, spindle, or turret.
This enables the equipment to:
-
Rotate 360° continuously
-
Maintain consistent airflow
-
Operate pneumatic tools or actuators at high speed
This is the fundamental working principle that allows pneumatic rotary unions to deliver stable airflow in dynamic motion environments.
Internal Structure of a Pneumatic Rotary Union
A typical pneumatic rotary union consists of the following components:
-
Housing (Stationary Body)
-
Rotating Shaft / Rotor
-
Bearings
-
Seals (O-rings, lip seals, or mechanical seals)
-
Passageways or chambers
-
End caps and fastening parts
-
Inlet and outlet ports
Each part contributes to the reliability, durability, and efficiency of the device.
Types of Pneumatic Rotary Unions
1. Single-Passage vs. Multi-Passage
Single-Passage: One air channel (common in simple indexing systems).
Multi-Passage: Up to 12 independent channels (used in complex automation).
2. Vacuum vs. Pressure Unions
Vacuum Unions: Designed to maintain suction integrity (e.g., pick-and-place robots).
Pressure Unions: Reinforced to handle compressed air surges.
3. Swivel Joints vs. Rotary Unions
Swivel Joints: Allow limited angular movement (±30°).
Rotary Unions: Enable unlimited 360° rotation.
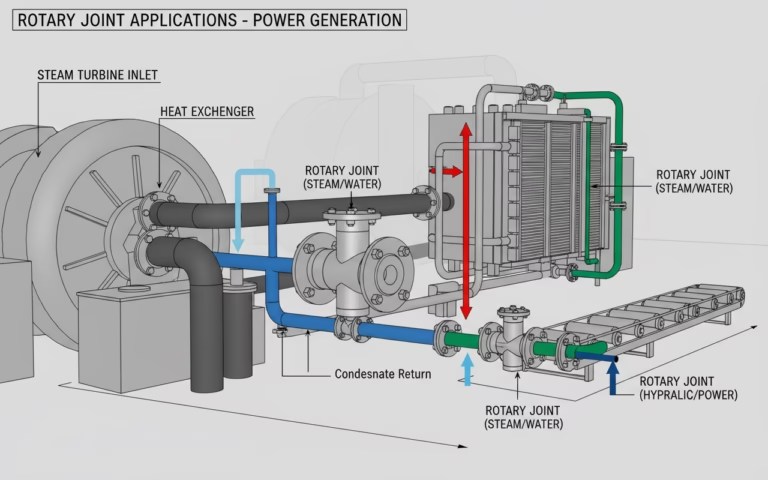
Applications of Pneumatic Rotary Unions
Pneumatic rotary unions are widely used across various industries where air-powered rotational equipment is essential.
1. CNC Machinery
-
Air clamping
-
Spindle cooling
-
Tool changing systems
2. Robotics
-
End-of-arm tooling
-
Grippers
-
Rotating manipulators
3. Packaging Machinery
-
Rotary filling machines
-
Bottle cappers
-
Labeling systems
4. Printing and Converting Equipment
-
Print rollers
-
Air cylinders
-
Web tension control
5. Automation and Assembly Lines
-
Pneumatic actuators
-
Pick-and-place systems
6. Textile Machinery
-
Dyeing cylinders
-
Air-operated brake systems
7. Food and Beverage Processing
-
Hygienic rotating equipment
-
Clean-in-place systems
The versatility of pneumatic rotary unions makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Advantages of Pneumatic Rotary Unions
1. Continuous 360° Rotation
Allows machinery to rotate without twisting air hoses.
2. Leak-Free Air Transfer
Precision seals prevent pressure loss.
3. High-Speed Operation
Optimized bearings support high-speed rotary motion.
4. Low Maintenance
Simple mechanical design reduces downtime.
5. Reduced Energy Consumption
Efficient sealing minimizes air leakage, lowering compressor load.
6. Versatile Configurations
Available in single, multi-passage, compact, and high-speed designs.
How to Choose the Right Pneumatic Rotary Union
Selecting the right rotary union involves evaluating the following factors:
1. Air Pressure Range
Ensure the rotary union can withstand maximum system pressure.
2. Rotational Speed (RPM)
High-speed applications require low-friction seals and special bearings.
3. Number of Passages
Multi-channel systems need isolated chambers.
4. Media Compatibility
Consider whether the rotary union must handle:
-
Compressed air
-
Vacuum
-
Nitrogen
-
Dry air or lubricated air
5. Installation Space
Compact designs are better for a limited mounting area.
6. Material Requirements
Common materials include:
-
Stainless steel
-
Aluminum
-
Brass
-
Carbon steel
7. Operating Environment
Identify exposure to:
-
Heat
-
Moisture
-
Dust
-
Chemicals
8. Duty Cycle and Runtime
Continuous operation requires stronger seals and more durable bearings.
Maintenance Tips for Pneumatic Rotary Unions
Proper maintenance ensures maximum service life:
-
Check seals regularly for wear
-
Inspect bearings for smooth rotation
-
Keep air filters clean to prevent contamination
-
Monitor operating temperature
-
Avoid excessive side-load on the shaft
-
Replace seals at recommended intervals
Routine inspection prevents unexpected failures and costly downtime.
Conclusion: Why Pneumatic Rotary Unions Matter
Pneumatic rotary unions are essential for transferring compressed air reliably in rotating applications. Their engineered design enables stable airflow, continuous rotation, and high-speed performance across a wide range of industries. Understanding how they work, their internal components, and their selection criteria ensures you choose the right rotary union for maximum efficiency, safety, and reliability.