How to maintain your hydraulic rotary joints for Optimal Performance: The Expert Guide
In the world of industrial machinery, hydraulic rotary joints are unsung heroes. These critical components are responsible for transferring pressurized hydraulic fluid from a stationary source to a rotating machine part, enabling the smooth and continuous operation of heavy-duty equipment. When a hydraulic rotary joint fails, it can lead to costly downtime, production losses, and potential safety hazards.
To help you protect your investment and maintain peak performance, we’ve created this expert guide on how to maintain your hydraulic rotary joints properly. Whether you’re an engineer, a technician, or a procurement manager, this comprehensive guide will provide you with the knowledge and actionable steps needed to extend the life of your equipment and prevent unexpected failures.
Introduction of Hydraulic Rotary Joints
Hydraulic rotary joints are integral components in industrial systems that allow the transfer of fluids or gases between stationary and rotating parts. These components are widely used in various applications such as manufacturing, construction, and energy production. Ensuring that these rotary joints are properly maintained is critical to maximizing their longevity and preventing costly failures.
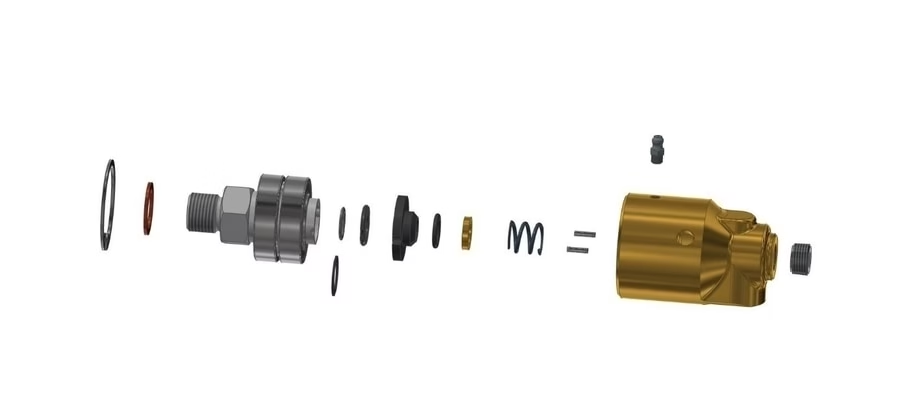
As a self-balancing element, the hydraulic rotary joint can transfer pressurized oil or other fluids to the hydraulic rotary cylinder, so that the piston of the equipment moves left and right, thereby achieving radial loosening of the power chuck. During the return stroke, the hydraulic rotary joint benefits from the pressure oil to release pressure, and resets through the action of the spring to achieve chuck clamping. The rotary seal part of the hydraulic rotary joint is installed on the core shaft of the equipment, and its main function is to form two independent sealing spaces to isolate the oil inlet chamber.
In this article, we will explore the essential Hydraulic rotary joint maintenance guide and best practices for maintaining Hydraulic rotary joint maintenance guide, focusing on preventing common failures, reducing downtime, and enhancing performance. We will also dive into key aspects like cleaning, lubrication, sealing, and monitoring to extend the life of hydraulic rotary joints. Hydraulic rotary joints
Hydraulic rotary joints
Understanding Hydraulic Rotary Joints and Their Role in Industrial Systems
Hydraulic rotary joints, also known as rotary unions or fluid swivels, are designed to transfer hydraulic fluids, steam, or other media to rotating equipment. They serve as the crucial interface that enables the transfer of hydraulic fluid between stationary supply lines and rotating machinery components. These precision components consist of carefully engineered seals, bearings, and flow passages that must work in harmony to maintain system integrity while allowing continuous rotation. These joints provide a continuous flow of fluid or gas to a rotating part, such as a drum or shaft, while maintaining a seal to prevent leaks.
Before we dive into maintenance, it’s crucial to understand what a hydraulic rotary joint does and the forces it withstands. A hydraulic rotary joint, also known as a hydraulic swivel joint or hydraulic rotary union, is a sealed device that allows for the rotation of machinery while maintaining a high-pressure fluid connection. They are essential in applications such as:
- Excavators and Cranes: For the continuous rotation of the cab and arm.
- Robotics: Providing hydraulic power to robotic arms and grippers.
- Machine Tools: Supplying coolant or hydraulic fluid to spindles and turrets.
- Agricultural Machinery: Enabling the operation of rotating components on harvesters and tractors.
The operational demands placed on these components are significant – they must withstand high pressures, varying temperatures, and continuous rotational stress while preventing leaks. Without properly functioning rotary joints, many automated systems would be impossible to operate efficiently, making their maintenance a critical aspect of overall system reliability.
Hydraulic rotary joints maintenance guide
1. Regular Inspection and Monitoring
One of the most critical aspects of maintaining hydraulic rotary joints is consistent and thorough inspection. Regular checks help identify any issues before they escalate into significant problems.
1.1 Establishing Inspection Protocols
The foundation of effective rotary joint maintenance is systematic inspection. Regular visual examinations should focus on:
🚨 Fluid Leakage
Watch for signs of fluid leakage or seepage around seals.
🔊 Unusual Noise or Vibration
Monitor for abnormal sounds or vibrations during operation.
♨️ Excessive Heat
Check for unusual heat generation at the joint interface.
🔄 Abnormal Resistance
Feel for irregular resistance during rotation.
🔩 Mounting & Connections
Inspect the condition of the mounting hardware and all connections.
1.2 Routine Inspection Tips for Hydraulic Rotary Joints
💧 Check for Leaks
Inspect connection points for hydraulic fluid leaks.
Leaks may indicate worn seals or component failure.
🛑 Inspect Seals
Seals can degrade due to pressure, temperature, or contamination.
Look for cracks, wear, or deformation.
👁️ Visual Inspection
Ensure no external debris or contaminants are present.
Keep the joint clean to maintain optimal performance.
Developing a consistent inspection schedule – daily quick checks, weekly detailed examinations, and monthly comprehensive inspections – helps identify developing issues before they lead to catastrophic failures. Even seemingly minor changes in performance can indicate the early stages of potential problems.
2. Lubrication and Greasing
Many hydraulic rotary joints incorporate separate lubrication systems for bearings and seals that are distinct from the main hydraulic fluid path. Proper lubrication is essential to reduce friction, prevent wear, and ensure smooth operation of hydraulic rotary joints. Using the right lubricant, as per the manufacturer’s specifications, will reduce the chances of overheating and corrosion.
Since the machine has not been used for a long time, it will directly cause scaling and rust inside the hydraulic rotary joint. Please note that if it is used again, it will be stuck or fall off. Please regularly fill oil with the oil filling device to ensure the reliability of the hydraulic rotary joint bearing operation.
Effective Lubrication Management for Rotary Unions
✅ Follow Manufacturer Guidelines
Use the correct type of grease or oil as recommended.
🔄 Lubricate Regularly
Maintain lubrication at specified intervals to prevent excessive friction and failure.
🛢️ Use High-Quality Lubricants
Ensure lubricant compatibility with system fluids for optimal performance.
🔧 Self-Lubricating? Still, Check!
Even self-lubricating rotary unions need periodic checks on lubricant conditions and levels.
⭐ Proper lubrication greatly extends the life of rotary unions by reducing friction and wear.
3. Maintaining Fluid Quality and Filtration
The quality of the hydraulic fluid used in the system directly impacts the performance of the rotary joints. Contaminants, such as dirt, water, and metal particles, can cause premature wear and failure of the seals and internal components. Keep the inside of the hydraulic rotary joint drum and the pipe clean. Special attention should be paid to new equipment, and filters should be added if necessary to avoid abnormal wear caused by foreign matter on the hydraulic rotary joint.
Hydraulic System Maintenance Tips
🧹 Use Filters
Install high-quality filters to block contaminants from entering the system.
🔄 Regular Fluid Changes
Replace hydraulic fluid at recommended intervals to prevent contamination buildup.
⚙️ Check Fluid Levels
Keep fluid levels within manufacturer guidelines to avoid air entry, pump cavitation, and potential system failure.
4. Temperature and Pressure Control
Hydraulic rotary joints operate optimally within specific temperature and pressure ranges. Maintaining these parameters is crucial to ensuring their longevity. The hydraulic rotary joint that circulates the hot medium should be heated gradually to avoid sudden changes in temperature. Check the wear and thickness change of the sealing surface of the hydraulic rotary joint (normal wear is 50×1773 10mm). Observe the friction track of the sealing surface to see if there are problems such as three-point discontinuity or scratches. If there are any of the above conditions, replace them immediately.
Pressure & Temperature Management Tips
📊 Monitor Pressure & Temperature
Use monitoring devices to maintain safe operating ranges.
❄️🔥 Avoid Temperature Extremes
Extreme heat or cold can accelerate seal wear and reduce joint lifespan.
🛡️ Install Pressure Relief Valves
Prevent system pressure from exceeding safe limits to avoid internal damage.
4.1 Pressure Management
Operating rotary joints at incorrect pressures is a common cause of premature failure.
Effective pressure management includes
✅ Verify Operating Pressure
Ensure pressures stay within the manufacturer’s specifications.
🛡️ Install Pressure Relief Systems
Prevent dangerous pressure spikes that can damage the system.
📈 Monitor Pressure Fluctuations
Watch for irregular changes that may signal potential issues.
🔄 Understand Pressure & Sealing
Know how pressure impacts sealing effectiveness for safe, reliable operation.
Most pneumatic systems operate at around 100 PSI, while hydraulic systems can range up to 3500 PSI. This significant difference highlights the importance of using components rated for the specific pressure range of your application.
4.2 Temperature Monitoring
Temperature affects the seal temperature.e Management involves
✅ Monitor Operating Temperatures
Track temperatures during normal operation.
🚨 Identify Abnormal Heat
Detect unusual heat increases that may signal friction issues.
💧 Control Fluid Temperatures
Keep hydraulic fluid within specified limits.
🔥 Protect from External Heat
Shield rotary joints from external heat sources when possible.
5. Proper Installation and Alignment
Installation & Alignment Best Practices
✅ Proper Installation
Always follow the manufacturer’s mounting guidelines to ensure correct setup.
🎯 Accurate Alignment
Ensure rotating and stationary parts are properly aligned to prevent uneven wear.
📉 Monitor Vibration
Watch for excessive vibration, which may signal misalignment or mounting issues.
⚠️ Misalignment and vibration can damage bearings, loosen hardware, and rapidly wear seals, leading to system failure.
Vibration Monitoring Best Practices
✅ Establish Baseline
Record normal vibration levels for future comparison.
🔄 Periodic Checks
Regularly monitor for vibration changes that may signal issues.
🎯 Correct Alignment
Fix alignment problems that can cause excessive vibration.
🛠️ Ensure Proper Mounting
Reduce transmitted vibration with secure, correct mounting.
🔍 Predictive Maintenance
Use vibration analysis to detect problems early and prevent failure.
6. Seal Maintenance and Replacement
Seals are crucial for maintaining pressure and preventing leaks in hydraulic rotary joints. Over time, seals wear down, become brittle, or break, causing fluid leaks and system malfunctions.
Seal Maintenance Tips for Hydraulic Rotary Joints
🔍 Regular Seal Inspections
Check seals frequently for wear, damage, or corrosion.
⚙️ Replace Damaged Seals
Promptly replace worn or damaged seals to prevent leaks and pressure loss.
🏷️ Use OEM Seals
Always use original manufacturer seals for proper fit and reliable performance.
7. System Pressure Balancing
Balancing the pressure within the hydraulic system is crucial for preventing damage to hydraulic rotary joints. Pressure imbalances can cause stress on seals and internal components.
Hydraulic Pressure Safety Tips
⚖️ Hydraulic Pressure Regulation
Keep system pressure within safe limits to prevent joint failure.
🛡️ Pressure Relief Valves
Install valves that activate when pressure exceeds safe levels, protecting the system from damage.
8. Training and Documentation
Training personnel on the importance of hydraulic rotary joint maintenance is critical for ensuring proper care. Additionally, maintaining comprehensive records of maintenance activities can help identify recurring issues and track the system’s health.
Operator Training & Record Keeping
👷 Operator Training
Equip operators and maintenance staff to spot early failure signs and perform proper maintenance.
🗂️ Keep Detailed Records
Maintain logs of inspections, repairs, and replacements for troubleshooting and system optimization.
9. Routine Performance Testing
Conducting performance tests can help detect inefficiencies or signs of wear that might not be visible during routine inspections.
Key Testing Methods for Hydraulic Rotary Joints
💧 Flow Testing
Verify flow rate matches specifications.
⚖️ Pressure Testing
Ensure the joint handles the required operational pressure without failure.
📊 Vibration Analysis
Monitor vibrations to detect misalignment or other issues early.
10. Maintenance Points for Compact Swivel Joint
To ensure long-term performance, safety, and durability of your compact swivel joint, follow these essential maintenance practices:
Keep the System Clean
Always keep the rotary joint drum and internal pipe surfaces clean during routine maintenance. Foreign particles such as dust, debris, or residues can cause abnormal wear, clogging, or internal scoring that leads to premature failure.
Install Filtration Devices
For newly installed equipment, it’s highly recommended to incorporate inline filters or strainers. These components help block contaminants from entering the rotary joint and the connected pipeline, significantly reducing the risk of internal damage.
Avoid Prolonged Downtime Without Use
If the equipment remains unused for an extended period, moisture and fluid residues may lead to internal rusting, scaling, or clogging. This can cause jamming, leakage, or increased torque when the system is reactivated. Regular operation or protective flushing can prevent these issues.
Perform Regular Lubrication
If your rotary joint includes an oiling or grease port, follow the manufacturer’s recommended lubrication schedule. Consistent oiling ensures smooth bearing operation, reduces friction, and helps prevent overheating or seizing during high-speed rotation.
Gradual Temperature Ramp-Up
When working with hot media such as steam, oil, or thermal fluids, always increase the system temperature gradually. Sudden thermal shock can cause seal deformation, metal fatigue, or even cracking of internal components.
Inspect the Sealing Surface Frequently
Monitor the sealing surface for signs of wear, reduced thickness, unusual friction marks, or scoring. Abnormalities in the seal face can lead to leaks or complete failure. Replace worn seals promptly to maintain pressure integrity and system efficiency.
Handle with Caution
Rotary joints are precision components. During installation, maintenance, or relocation, avoid any physical impacts. Dropping or knocking the unit may result in internal misalignment, cracks, or performance degradation.
Prevent Foreign Material Intrusion
Never allow foreign materials—such as metal shavings, sand, or liquids—to enter the rotary joint. These contaminants can cause seal abrasion, unbalanced rotation, or even catastrophic failure during operation. Always cover open ports during storage or downtime.
By implementing these proactive maintenance steps, you’ll extend the service life of your compact swivel joint and ensure optimal performance in your application, whether in hydraulic systems, robotics, packaging machinery, or rotating automation tools.
Addressing Common Failure Modes
1. Seal Deterioration and Failure
Seals are perhaps the most vulnerable components in hydraulic rotary joints.
Common Causes of Seal Failure & Prevention
❌ Causes of Seal Failure
Natural aging and wear
Chemical incompatibility with fluids
Excessive temperature exposure
Operating beyond pressure limits
Contamination damage
🛡️ Prevention Strategies
Choose the right seal materials for your application
Maintain fluid cleanliness
Monitor operating temperatures
Replace seals before critical wear
2. Bearing Issues
Bearings support the rotational elements while maintaining proper alignment.
Common Bearing Issues & Prevention
⚠️ Common Issues
Inadequate lubrication → Excessive friction
Contamination → Accelerated wear
Misalignment → Uneven loading
Excessive loads beyond specs
Vibration damage over time
🛠️ Prevention Tips
Regular bearing inspection
Proper lubrication
Verify correct alignment
Monitor early signs: noise & heat
3. Fluid-Related Problems
Hydraulic Fluid Quality & Its Impact
⚠️ Issues from Poor Fluid Quality
Contamination → Accelerated seal & surface wear
Wrong viscosity → Poor flow & lubrication
Fluid degradation → Reduced lubrication effectiveness
Water or air presence → Erratic operation
Chemical breakdown → Seal damage
🛡️ Prevention Tips
Regular fluid analysis
Use proper filtration
Schedule a timely fluid replacement
Ensure fluid compatibility with seals
Installation and System Design Considerations
1. Proper Mounting and Alignment
Installation Tips for Rotary Joint Longevity
✅ Follow the manufacturer’s Torque Specs
Ensure mounting hardware is tightened correctly.
🎯 Verify Alignment
Align the stationary and rotating parts precisely.
↔️ Minimize Side Loading
Avoid lateral forces on the rotary joint.
🔧 Provide Adequate Support
Support both the joint and connected components.
⚠️ Address Misalignment Promptly
Fix alignment issues immediately to prevent damage.
Many rotary joint failures can be traced back to improper initial installation. Taking time to ensure correct mounting and alignment pays dividends through extended service life.
2. Managing Rotational Requirements
Best Practices for Flexible Supply Lines to Rotary Joints
➰ Provide Service Loops
Allow enough slack to accommodate rotation.
🛠️ Proper Line Support
Prevent stress on connections with secure supports.
✅ Use Rated Flexible Hoses
Choose hoses suitable for your specific application.
🛡️ Protect Supply Lines
Guard against mechanical damage.
🔄 Manage Rotation
Consider rotation limits or continuous rotation needs.
For applications requiring limited rotation (less than 360 degrees), a flexible hose with a service loop may be sufficient. For continuous or unlimited rotation, specialized rotary unions are essential.
3. Environmental Protection
Environmental Protection for Rotary Joints
🛡️ Shield from Dirt, Dust & Moisture
Keep contaminants away to ensure smooth operation.
♨️ Provide Thermal Protection
Guard against extreme temperatures.
⚠️ Prevent Corrosive Exposure
Avoid contact with harmful chemicals.
🚧 Protect from Impact & Damage
Safeguard joints from mechanical harm.
🍂 Address Seasonal Variations
Adjust maintenance for changing operating conditions.
Simple protective measures often deliver substantial improvements in service life and reliability, particularly in harsh industrial environments.
Developing a Comprehensive Maintenance Schedule
1 . Daily Checks
Quick Checks for Rotary Joint SOP
🔎 Visual Inspection
Look for leaks or unusual conditions.
👂 Listen Carefully
Detect abnormal sounds during operation.
📊 Monitor Parameters
Check pressure and temperature regularly.
🔄 Verify Rotation
Ensure smooth and normal rotation behavior.
These daily checks require minimal time investment but provide valuable early warning of developing issues.
2. Weekly Maintenance Tasks
🔍 Inspect Seals
Check sealing areas for signs of weeping or leaks.
🧼 Clean Surfaces
Clean external parts and inspection ports.
🔧 Verify Hardware
Ensure mounting bolts and hardware are tight.
📈 Record Data
Log operating parameters for trend analysis.
Weekly maintenance creates opportunities to catch developing issues before they progress to serious problems.
3 . Monthly Procedures
Comprehensive Rotary Joint Evaluation
✅ Full Component Inspection
Examine all accessible parts thoroughly.
🛢️ Lubrication Service
Perform lubrication as per the manufacturer’s guidelines.
💧 Fluid Condition Check
Verify the cleanliness and quality of hydraulic fluid.
⚠️ Check Alignment & Wear
Identify misalignment or excessive wear early.
Monthly maintenance provides deeper insights into component health and enables planning for more extensive maintenance actions if needed.
4 . Annual Overhaul Considerations
Major Maintenance During Planned Shutdowns
🔧 Complete Disassembly & Inspection
A thorough check of all parts, where possible.
🔄 Replace Worn Components
Follow service schedules for part replacement.
📏 Verify Dimensions & Tolerances
Ensure critical measurements are within specs.
🧪 Controlled Testing
Test under controlled conditions before restart.
📋 Document Findings
Keep detailed records for future reference.
Annual maintenance activities may require manufacturer involvement or specially trained personnel, particularly for high-performance or critical applications.
Advanced Maintenance Techniques of
1 . Implementing Predictive Maintenance of
Condition-Based Maintenance Techniques
📈 Vibration Analysis
Detect bearing degradation early.
🌡️ Infrared Thermography
Identify developing heat-related issues.
🛢️ Oil Analysis
Monitor contamination and wear particles.
📊 Performance Trending
Track gradual equipment degradation.
🎧 Acoustic Monitoring
Early detection of internal faults via sound.
These techniques allow maintenance to be performed based on actual component conditions rather than arbitrary schedules, potentially extending service intervals while maintaining reliability.
2 . Specialized Tools and Equipment for Hydraulic Rotary Joint Maintenance Guide
Specialized Tools for Effective Maintenance
⚖️ Pressure Testing Equipment
Verify seal integrity reliably.
🎯 Alignment Tools
Ensure precise installation.
🔧 Torque Wrenches
Achieve accurate fastener tightening.
💧 Flow Meters
Check performance flow characteristics.
🌡️ Temperature Devices
Monitor thermal conditions precisely.
Investing in appropriate tools ensures maintenance tasks are performed correctly and consistently, reducing the risk of errors that could lead to premature component failure.
Special Considerations for High-Demand Applications
1 . High-Pressure Systems
Maintenance Tips for High-Pressure Applications
⏱️ Frequent Inspections
Increase inspection intervals for safety.
🛡️ Enhanced Filtration
Use superior filtration systems.
🔄 Pressure Cycling Awareness
Consider the effects of pressure fluctuations.
✅ Safety Margins
Select components with appropriate safety factors.
📊 Enhanced Monitoring
Closely track operating parameters.
High-pressure applications place exceptional demands on sealing systems and structural components, necessitating more rigorous maintenance approaches.
2 . Continuous Operation Applications
Maintenance Strategies for Continuous Operation Systems
📡 Design for Online Monitoring
Enable real-time system health tracking.
🔁 Implement Redundant Systems
Ensure backup components, where possible.
⚡ Quick-Change Procedures
Develop fast replacement methods for critical parts.
📈 Enhanced Predictive Maintenance
Maximize the effectiveness of planned upkeep.
🎓 Specialized Training
Equip maintenance staff with targeted skills.
Planning for maintenance in continuous operations requires balancing production requirements with component longevity considerations.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
1 . Identifying and Resolving Leaks
Common Rotary Joint Leak Issues & Solutions
🔍 Leak Source Tracking
Identify if from a static seal, a dynamic seal, or a housing crack.
⏳ Leakage Timing
Check if the leak is continuous or operation-specific.
🔧 Connection Tightness
Verify that all fittings and mounting hardware are secure.
🛡️ Seal Condition
Inspect for damage or contamination.
📋 Operating Conditions
Ensure parameters are within specs.
⚠️ Prompt Action
Prevent fluid loss, contamination, and safety risks by timely fixing leaks.
2 . Addressing Excessive Resistance
Troubleshooting Rotary Joint Resistance to Rotation
🛢️ Lubrication Check
Ensure bearings and seals are properly lubricated.
🎯 Alignment Verification
Confirm the correct alignment of connected components.
🧹 Debris Inspection
Look for contamination affecting movement.
🔧 Installation Review
Check for binding or side-loading issues.
📊 Operating Pressure
Verify pressures are within specifications.
Excessive resistance not only affects system performance but can also lead to accelerated wear and eventual component failure if not addressed.
Conclusion
Hydraulic rotary joints play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth operation of industrial systems. By following the Hydraulic rotary joint maintenance guide in this article, such as regular inspections, proper lubrication, seal maintenance, and pressure and temperature control, you can significantly extend the lifespan of these components and prevent costly failures.
Adhering to a structured maintenance routine not only ensures the efficiency of the system but also reduces unexpected downtime, enhances safety, and lowers repair costs. By integrating these Hydraulic rotary joint maintenance guides and maintenance strategies, industries can optimize their hydraulic rotary joints’ performance and reliability, keeping their operations running smoothly and efficiently.